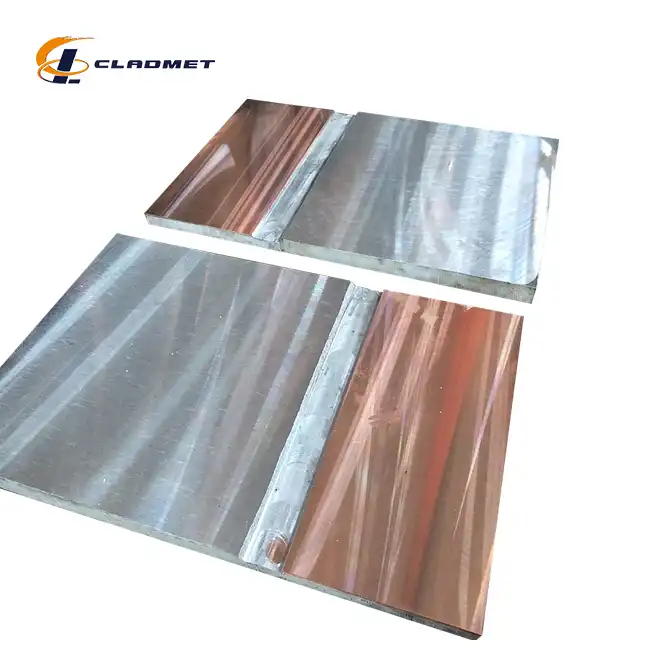
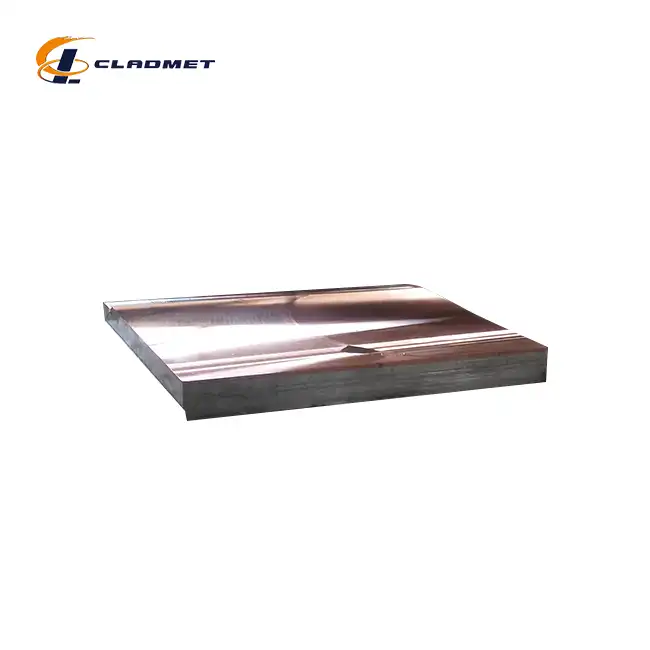
Why are Clad Plates Used in Tube Sheets?
 2025-02-19 13:22:50
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:50
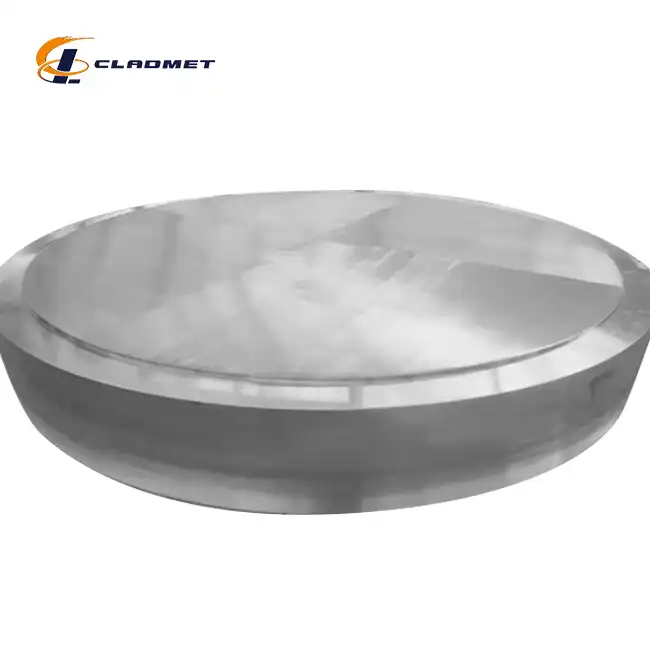
View:389Tube sheets are critical components in heat exchangers and other industrial equipment where they serve as the foundation for securing and supporting multiple tubes. The use of clad plates for tube sheets has become increasingly prevalent in modern industrial applications due to their unique combination of mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. Clad plates, which consist of a base metal bonded with a corrosion-resistant layer, offer an optimal solution for environments where both structural integrity and chemical resistance are paramount. This comprehensive analysis explores the various aspects of clad plates for tube sheets and their essential role in industrial applications.

Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Superior Performance
Explosive Welding Technology
The explosive welding process represents a breakthrough in the manufacturing of clad plates for tube sheets. This sophisticated technique involves carefully positioning two dissimilar metals and using controlled detonation to create a metallurgical bond. The process generates a high-velocity collision between the materials, resulting in an exceptionally strong atomic-level bond. At Baoji JL Clad Metals, the explosive welding process is optimized for materials ranging from 3mm to 300mm in thickness, with width capabilities extending up to 5,000mm. This method is particularly advantageous for creating clad plates that must withstand extreme pressure conditions in petrochemical processing and marine applications.
Roll Bonding Precision
Roll bonding technology has revolutionized the production of clad plates for tube sheets by offering unprecedented control over the bonding process. This method employs specialized rolling equipment that applies precise pressure to join the base metal and cladding material. The process involves multiple passes through carefully calibrated rollers, ensuring uniform bonding across the entire surface. The technique is particularly effective for materials like titanium, nickel, and stainless steel cladding on carbon steel bases. The resulting products demonstrate exceptional thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making them ideal for heat exchanger applications.
Hot Isostatic Pressing Innovation
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) represents the cutting edge of clad plate manufacturing technology. This process involves subjecting the materials to simultaneous high pressure and elevated temperatures in a controlled environment. The combination of heat and pressure promotes atomic diffusion between the base metal and cladding layer, creating an extraordinarily strong metallurgical bond. This method is particularly effective for complex material combinations and has been instrumental in meeting the stringent requirements of GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS standards.
Material Selection and Performance Characteristics
Advanced Material Combinations
The selection of materials for clad plates in tube sheets involves careful consideration of both the base metal and cladding layer. The base metals typically include carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, chosen for their structural integrity and cost-effectiveness. The cladding materials encompass a wide range of high-performance metals including titanium, nickel alloys, stainless steel, aluminum, tantalum, and zirconium. Each combination is engineered to meet specific performance requirements, with particular attention paid to corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength in demanding industrial environments.
Enhanced Corrosion Protection
Corrosion resistance stands as a paramount feature of clad plates for tube sheets, particularly in aggressive chemical environments. The cladding layer, often composed of specialized alloys, provides an impenetrable barrier against corrosive media while the base metal maintains structural integrity. This dual-layer protection system has proven especially valuable in applications involving seawater, aggressive chemicals, and high-temperature processes. The surface treatment options, including polishing and corrosion-resistant coatings, further enhance the protective properties of these materials.
Thermal Performance Optimization
The thermal characteristics of clad plates for tube sheets play a crucial role in their industrial application. The carefully selected material combinations ensure optimal heat transfer while maintaining structural integrity under thermal cycling conditions. This is particularly important in heat exchanger applications where efficient thermal conductivity directly impacts system performance. The plates demonstrate exceptional stability across a wide temperature range, making them suitable for both cryogenic and high-temperature applications.\

Industrial Applications and Implementation
Chemical Processing Solutions
In chemical processing applications, clad plates for tube sheets face some of the most demanding operating conditions. These components must withstand aggressive chemicals while maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. The combination of corrosion-resistant cladding materials with strong base metals provides an ideal solution for chemical processing equipment. The plates are manufactured to meet specific industry standards, including ASME/ASTM requirements, ensuring reliable performance in critical chemical processing operations.
Oil and Gas Industry Applications
The oil and gas sector presents unique challenges for tube sheet materials, including exposure to corrosive hydrocarbons and high-pressure environments. Clad plates have proven exceptionally effective in these applications, offering superior resistance to both chemical attack and mechanical stress. The plates are manufactured with precise dimensional tolerances and undergo rigorous quality control to ensure compliance with industry standards. This attention to detail has made them a preferred choice for offshore platforms, refineries, and processing facilities.
Power Generation Requirements
Power generation facilities require tube sheets that can withstand high temperatures, pressures, and corrosive environments while maintaining excellent heat transfer properties. Clad plates meet these demanding requirements through their unique combination of materials and manufacturing processes. The plates are engineered to provide long-term reliability in both conventional and nuclear power applications, with special attention paid to quality control and certification requirements.
Conclusion
The implementation of clad plates for tube sheets represents a significant advancement in industrial equipment design, offering an optimal balance of performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Their success stems from the combination of advanced manufacturing techniques, carefully selected materials, and rigorous quality control processes. Looking to enhance your industrial operations with high-quality clad plates? Baoji JL Clad Metals stands ready to serve your needs with our state-of-the-art manufacturing capabilities, comprehensive international certifications (ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS), and commitment to innovation. Our expertise in explosive composite technology, coupled with global sales coverage and customization options, ensures we can meet your specific requirements. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our advanced clad plate solutions can benefit your operations.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Materials in Heat Exchanger Design: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-251.
2. Zhang, L., et al. (2023). "Metallurgical Bonding Mechanisms in Explosion-Welded Clad Plates." Materials Science and Technology, 39(8), 1122-1138.
3. Anderson, M.H. & Roberts, S.D. (2022). "Performance Analysis of Clad Materials in Corrosive Environments." Corrosion Science, 184, 109-127.
4. Wilson, R.T. (2023). "Thermal Performance of Bimetallic Plates in Industrial Heat Exchangers." International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 188, 77-92.
5. Thompson, D.A. & Lee, K.S. (2023). "Manufacturing Processes for High-Performance Clad Materials." Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 85, 156-171.
6. Chen, H., et al. (2024). "Quality Control Standards for Clad Plate Production in Industrial Applications." Quality Engineering, 36(2), 89-104.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)