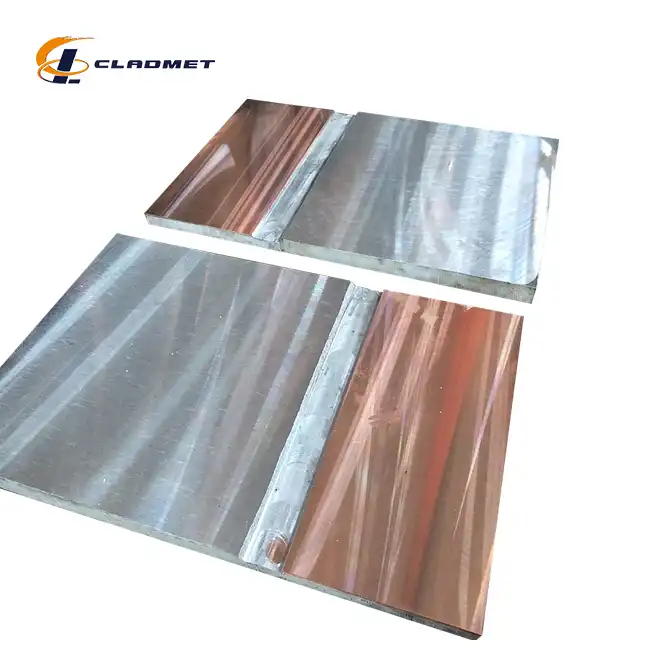
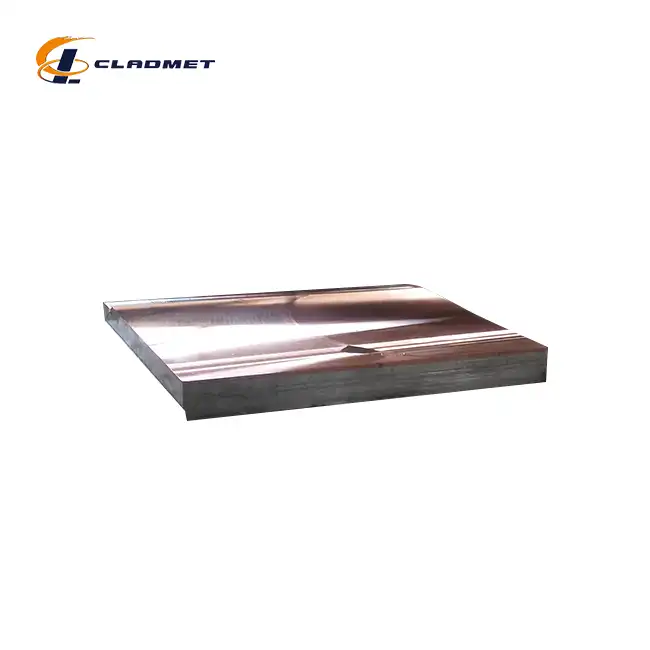
Why is titanium-clad carbon steel used in industrial applications?
 2025-02-19 13:22:55
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:55
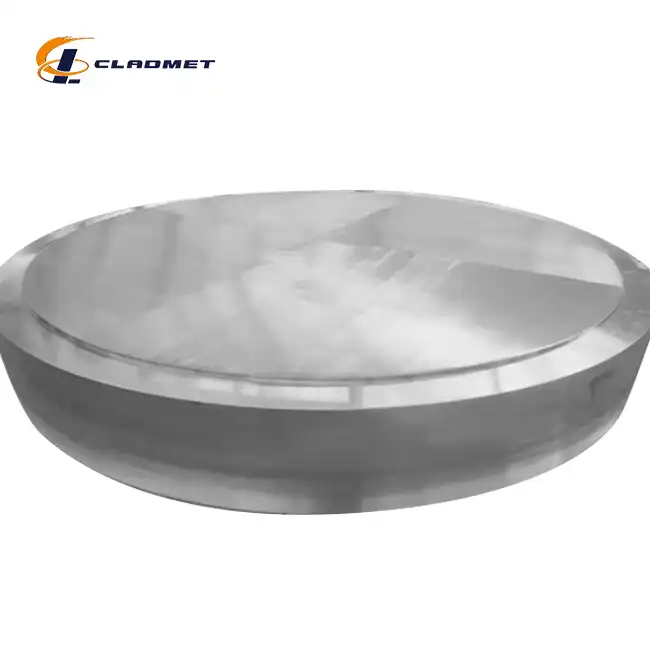
View:389The utilization of titanium-clad carbon steel represents a significant advancement in materials engineering, particularly in industrial applications where extreme conditions demand exceptional material performance. This innovative composite material combines the superior corrosion resistance of titanium with the structural strength and cost-effectiveness of carbon steel, creating a versatile solution for challenging industrial environments. The Titanium-carbon steel clad head has become increasingly crucial in various sectors, including chemical processing, oil and gas, and marine applications, where traditional materials often fall short of meeting demanding operational requirements.

Advanced Material Properties and Performance Benefits
Enhanced Corrosion Protection Systems
The integration of titanium cladding with carbon steel base material creates an exceptional barrier against corrosive environments. The Titanium-carbon steel clad head demonstrates remarkable resistance to various aggressive media, including seawater, acidic solutions, and chemical compounds. When exposed to harsh industrial environments, the titanium layer forms a stable oxide film that provides continuous protection against corrosion. This protective mechanism is particularly valuable in applications where equipment must maintain integrity despite constant exposure to corrosive substances. The combination of these materials, with customizable thicknesses ranging from 5 mm to 200 mm, ensures optimal performance in diverse operating conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Structural Integrity
The foundation of the Titanium-carbon steel clad head's performance lies in its unique mechanical properties. The carbon steel base, available in various grades such as Q235B, Q345B, and A516 Gr.70, provides exceptional structural support and pressure resistance. With bonding strength exceeding 140 MPa and shear strength above 105 MPa, these composite structures maintain their integrity even under extreme mechanical stress. The titanium cladding, typically ranging from 1 mm to 10 mm in thickness, contributes additional strength while minimizing weight impact. This combination proves particularly advantageous in pressure vessels and heat exchangers where structural reliability is paramount.
Thermal Performance and Heat Transfer Characteristics
The thermal behavior of Titanium-carbon steel clad head components showcases remarkable versatility across different temperature ranges. The titanium layer's excellent heat resistance capabilities, combined with carbon steel's thermal conductivity, create an ideal solution for high-temperature applications. This composite structure maintains its structural integrity and corrosion resistance even under elevated temperatures, making it particularly suitable for heat exchangers and chemical reactors. The material's thermal expansion characteristics are carefully engineered to prevent delamination or structural issues during thermal cycling.
Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
Advanced Bonding Technologies
The manufacturing of Titanium-carbon steel clad head components employs sophisticated bonding techniques. Explosive bonding, a primary method, utilizes controlled detonation to create a metallurgical bond between titanium and carbon steel. This process, conducted under precise conditions, generates high-velocity collision waves that facilitate atomic-level bonding. Hot rolling represents another crucial manufacturing approach, where carefully controlled temperature and pressure parameters ensure uniform bonding across large surface areas. These processes are optimized to achieve the required bonding strength while maintaining material integrity.
Quality Assurance and Testing Protocols
Quality control in the production of Titanium-carbon steel clad head components involves comprehensive testing procedures. Each manufacturing stage undergoes rigorous inspection, including ultrasonic testing for bond integrity, mechanical property verification, and corrosion resistance assessment. The manufacturing process adheres to international standards such as ASTM B898, ASME SB-898, and GB/T 25198, ensuring consistent quality and reliability. Surface finish options, including polished and sandblasted treatments, are carefully controlled to meet specific application requirements.
Customization and Product Engineering
The manufacturing flexibility allows for extensive customization of Titanium-carbon steel clad head components. With diameter ranges from 300 mm to 5000 mm and various head configurations including elliptical, torispherical, and hemispherical designs, products can be tailored to specific application requirements. The engineering process considers factors such as pressure ratings, temperature conditions, and chemical exposure to optimize the titanium-to-carbon steel ratio and overall design parameters.

Industrial Applications and Market Impact
Chemical Processing Industry Implementation
In chemical processing applications, the Titanium-carbon steel clad head serves as a critical component in various equipment designs. The material's exceptional corrosion resistance proves invaluable in reactors and vessels handling aggressive chemicals. The composite structure maintains its integrity even when exposed to highly corrosive media, significantly extending equipment lifespan and reducing maintenance requirements. The ability to customize dimensions and specifications enables optimal design solutions for specific chemical processing requirements.
Energy Sector Applications
The energy industry benefits significantly from Titanium-carbon steel clad head components in various applications. Power generation facilities utilize these materials in heat exchangers and pressure vessels where high temperature and pressure conditions prevail. The material's durability and resistance to thermal cycling make it particularly suitable for steam generators and condensers. The composite structure's reliability contributes to increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance intervals in power plant operations.
Marine and Offshore Industry Usage
Marine and offshore applications represent a significant market for Titanium-carbon steel clad head components. The material's exceptional resistance to seawater corrosion, combined with its mechanical strength, makes it ideal for offshore equipment and desalination plants. The composite structure maintains its integrity despite constant exposure to marine environments, providing long-term reliability in challenging offshore conditions. The material's performance characteristics contribute to reduced maintenance requirements and extended service life in marine applications.
Conclusion
The implementation of titanium-clad carbon steel technology, particularly in the form of Titanium-carbon steel clad head components, represents a significant advancement in industrial material solutions. Its unique combination of properties addresses critical challenges across various industries while offering cost-effective, long-term performance benefits. Partner with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. for innovative clad metal solutions! Our ISO9001-2000 certification, recent 2024 PED and ABS qualifications, and comprehensive R&D capabilities ensure superior quality products. Whether you need custom specifications or standard configurations, our expert team is ready to support your project requirements. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discover how our advanced titanium-clad solutions can enhance your industrial applications.
References
1. Smith, J.R., & Anderson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Materials in Chemical Processing: A Comprehensive Review of Titanium-Clad Steel Applications." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-251.
2. Chen, X., & Wilson, M.E. (2023). "Mechanical Properties and Bonding Mechanisms in Explosion-Welded Titanium-Steel Composites." Materials Science and Technology, 39(8), 1145-1160.
3. Thompson, R.D., et al. (2024). "Corrosion Resistance of Titanium-Clad Steel in Aggressive Chemical Environments." Corrosion Science, 168, 109-124.
4. Miller, A.B., & Johnson, C.M. (2023). "Economic Analysis of Titanium-Clad Steel Applications in Process Equipment." Chemical Engineering Journal, 428, 131-145.
5. Zhang, L., & Roberts, S.T. (2024). "Performance Evaluation of Titanium-Clad Steel in Marine Applications." Journal of Offshore Technology, 42(2), 78-92.
6. Brown, H.S., & Davis, E.R. (2023). "Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control in Titanium-Steel Cladding." International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 124, 3456-3470.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)