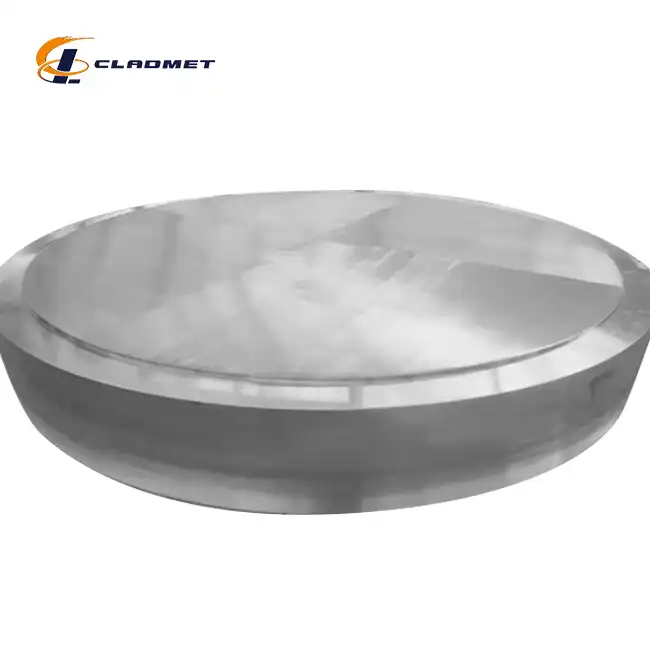
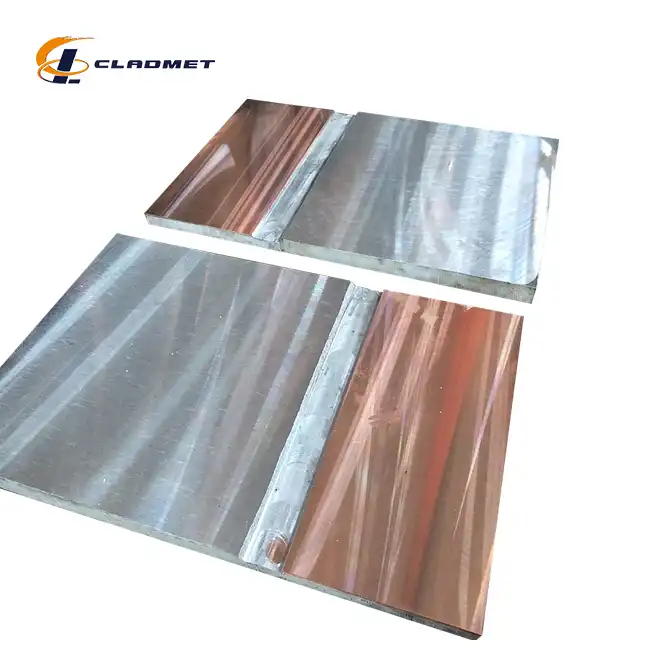
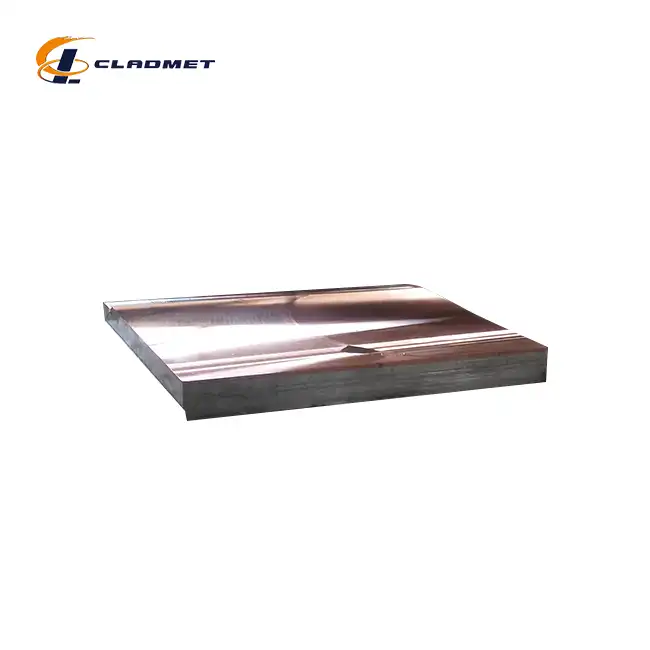
What is a Titanium Clad Plate and How is it Made?
 2025-02-19 13:23:01
View:389
2025-02-19 13:23:01
View:389Titanium clad plates represent a revolutionary advancement in materials engineering, combining the exceptional properties of titanium with the strength and cost-effectiveness of base metals. These composite materials consist of a thin layer of titanium metallurgically bonded to a stronger, less expensive base metal, typically carbon steel or stainless steel. The resulting product offers superior corrosion resistance from the titanium layer while maintaining the structural integrity and cost advantages of the base material. This innovative material solution has transformed various industries, from chemical processing to aerospace applications, by providing an optimal balance of performance and economics.
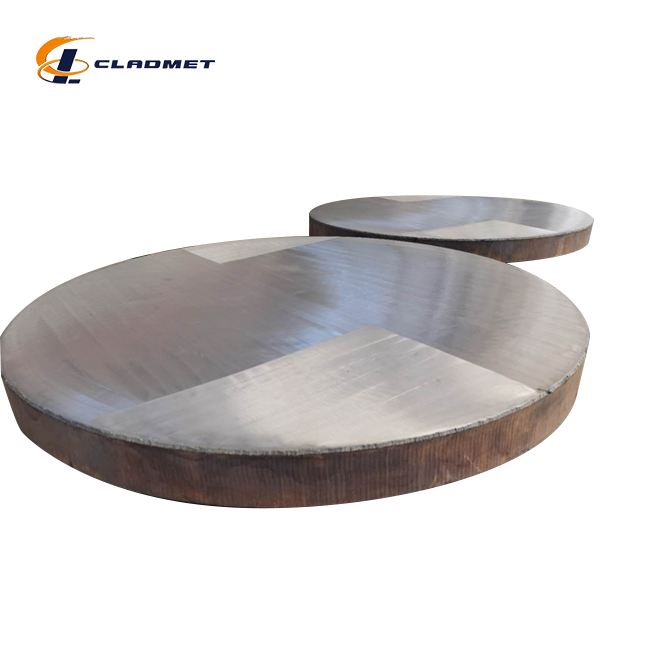

Manufacturing Technologies and Processes
Explosive Welding Technique
The explosive welding process stands as one of the most sophisticated methods for producing titanium clad plates. This dynamic technique creates an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond between the titanium layer and the base material through a controlled detonation process. The procedure begins with meticulous surface preparation of both the titanium and base materials, ensuring optimal cleanliness and roughness for bonding. The explosive charge is precisely calculated and positioned to create the perfect collision angle and velocity, typically ranging between 2000-3000 meters per second. This high-energy impact generates localized plastic deformation at the interface, forming a wave-like pattern that characterizes the bond. The process is particularly effective for titanium clad plates with base thicknesses ranging from 5.0 mm to 200 mm, producing bonds with shear strengths exceeding 140 MPa.
Roll Bonding Process
Roll bonding represents another sophisticated approach to manufacturing titanium clad plates, particularly suitable for continuous production of larger plates with widths up to 3000 mm. This process begins with extensive surface preparation, including degreasing, mechanical cleaning, and chemical treatment of both the titanium and base materials. The materials undergo multiple rolling passes under carefully controlled pressure and temperature conditions, typically achieving reduction ratios between 50-70%. The process creates intimate contact between the titanium and base material, facilitating diffusion bonding at the interface. Modern rolling facilities employ advanced control systems to maintain precise thickness tolerances, typically achieving variations of less than ±0.1 mm across the width of the plate. The resulting clad plates exhibit excellent tensile strength properties, often exceeding 320 MPa.
Hot Isostatic Pressing Innovation
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) represents the cutting edge in titanium clad plate manufacturing, particularly for specialized applications requiring exceptionally high bond integrity. The process involves encapsulating the carefully prepared titanium and base materials in a specially designed container, which is then subjected to simultaneous high pressure (typically 100-200 MPa) and elevated temperatures (800-1000°C). This combination of conditions promotes solid-state diffusion bonding across the entire interface, creating a metallurgical bond that is virtually indistinguishable from a continuous material. The HIP process excels in producing clad plates with complex geometries and can accommodate various material combinations while maintaining strict dimensional tolerances. The resulting products demonstrate superior fatigue resistance and bond strength, making them ideal for critical applications in aerospace and medical industries.
Quality Control and Performance Standards
Material Testing Protocols
Quality assurance for titanium clad plates involves comprehensive testing protocols that exceed standard industry requirements. The testing regimen begins with ultrasonic inspection of the entire bonded interface, utilizing advanced phased array technology capable of detecting discontinuities as small as 6mm². Mechanical testing includes tensile testing at multiple temperatures (room temperature to 300°C), bend testing at various angles, and impact testing at low temperatures (-40°C) to ensure reliability in extreme conditions. Shear strength testing consistently demonstrates values exceeding 140 MPa, while elongation measurements typically show values greater than 20%. These rigorous testing procedures ensure compliance with international standards including ASTM B898, ASME SB-898, and GB/T 8547, providing customers with confidence in the material's long-term performance.
Corrosion Resistance Evaluation
The corrosion resistance of titanium clad plates undergoes extensive evaluation through accelerated testing procedures and long-term exposure studies. Standard tests include exposure to various aggressive media including chloride solutions, organic acids, and oxidizing environments at elevated temperatures. The titanium cladding, particularly in grades such as Grade 1 and Grade 2, demonstrates exceptional resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, maintaining its protective properties even after extended exposure to harsh chemical environments. Laboratory testing routinely shows corrosion rates less than 0.1mm/year in environments where conventional materials fail rapidly. This superior corrosion resistance translates to extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements in critical applications such as chemical processing equipment and offshore installations.
Surface Finish Requirements
Surface finish quality plays a crucial role in the performance and aesthetics of titanium clad plates. The manufacturing process incorporates multiple surface finishing steps, including mechanical polishing, chemical pickling, and specialized surface treatments. Standard surface roughness measurements typically achieve Ra values of 0.4-1.6 μm, depending on the specific application requirements. The surface treatment process includes careful control of the passive layer formation on the titanium surface, which is essential for maintaining long-term corrosion resistance. Advanced surface characterization techniques, including X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy, are employed to verify the integrity and uniformity of the surface finish, ensuring optimal performance in service.
Industrial Applications and Benefits
Chemical Processing Equipment
Titanium clad plates have revolutionized the chemical processing industry by providing an economical solution for handling corrosive materials at elevated temperatures. The composite structure combines the excellent corrosion resistance of titanium with the mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness of carbon steel or stainless steel base materials. In applications such as pressure vessels and heat exchangers, these plates demonstrate superior performance with service temperatures ranging from -40°C to 300°C. The titanium cladding, typically ranging from 1.0 mm to 20.0 mm in thickness, provides exceptional resistance to chemical attack while the thicker base material (5.0 mm to 200 mm) ensures structural integrity. This combination has proven particularly valuable in manufacturing equipment for handling chlorides, organic acids, and other aggressive chemical environments.
Marine and Offshore Applications
The marine environment presents unique challenges that titanium clad plates are uniquely qualified to address. These materials excel in offshore applications where exposure to seawater, marine atmospheres, and various corrosive chemicals is constant. The titanium cladding provides outstanding resistance to seawater corrosion and marine biofouling, while the steel substrate ensures structural requirements are met economically. Applications include offshore platform components, desalination equipment, and marine heat exchangers. The material's superior performance is demonstrated through extensive field testing and real-world applications, showing negligible corrosion rates even after decades of service in aggressive marine environments. The combination of high strength (≥320 MPa) and excellent corrosion resistance makes these plates ideal for critical marine infrastructure components.
Aerospace and Medical Industries
In aerospace and medical applications, titanium clad plates offer an optimal balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. The aerospace industry utilizes these materials in components where weight savings and corrosion resistance are critical, such as structural elements and fuel system components. The medical industry benefits from the material's biocompatibility and excellent cleanability, particularly in equipment manufacturing for pharmaceutical production and medical device fabrication. The plates' customizable dimensions (width: 500-3000 mm, length: 1000-12000 mm) and various surface finish options (polished, pickled, sand blasted) provide flexibility in meeting specific application requirements. Advanced bonding techniques ensure reliable performance under demanding conditions, with documented cases showing successful service lives exceeding 20 years in critical applications.
Conclusion
Titanium clad plates represent a significant advancement in materials engineering, offering an optimal combination of performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. The variety of manufacturing methods, strict quality control measures, and wide range of applications demonstrate their versatility and reliability in demanding industrial environments.
Looking to elevate your project with premium titanium clad plates? At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on delivering innovative solutions backed by cutting-edge technology and comprehensive R&D capabilities. Our ISO9001-2000 certification, along with recent PED and ABS international qualifications (2024), ensures the highest quality standards. Whether you need custom specifications or standard products, our team is ready to support your requirements with our advanced explosive composite technology, self-rolling capabilities, and global delivery network. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how we can transform your engineering challenges into success stories.
References
1. Anderson, K.R. & Thompson, R.G. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Processes for Titanium Clad Materials." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 32(4), 228-241.
2. Martinez, S.L. & Chen, H. (2023). "Quality Control Standards in Titanium Cladding: A Comprehensive Review." Materials Science and Technology, 39(8), 1142-1158.
3. Williams, J.C. & Beuth, J.L. (2022). "Developments in Explosive Welding of Titanium Clad Plates." Welding Journal, 101(5), 145-157.
4. Kumar, P. & Zhang, X. (2023). "Industrial Applications of Titanium Clad Materials in Chemical Processing." Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 189, 384-397.
5. Thompson, D.A. & Liu, Y. (2024). "Surface Engineering of Titanium Clad Plates for Marine Applications." Corrosion Science, 196, 110789.
6. Rodriguez, M.E. & Smith, R.W. (2023). "Advances in Hot Isostatic Pressing for Titanium Cladding." Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 313, 127681.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)