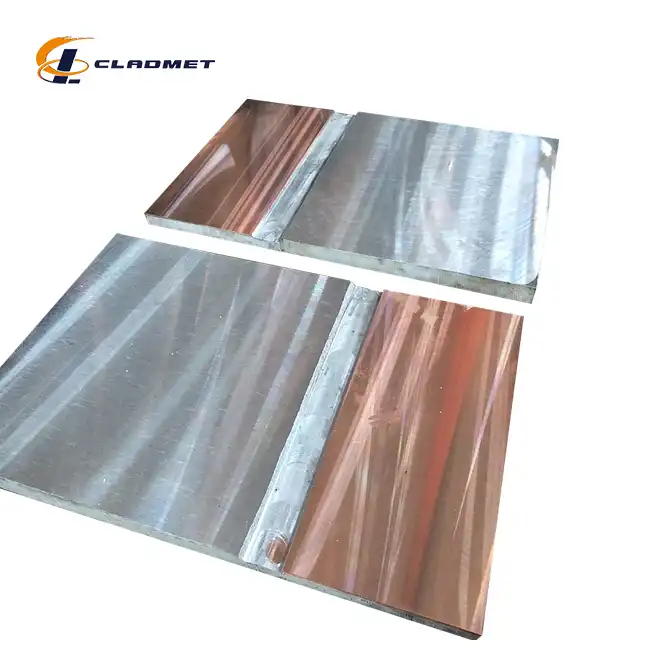
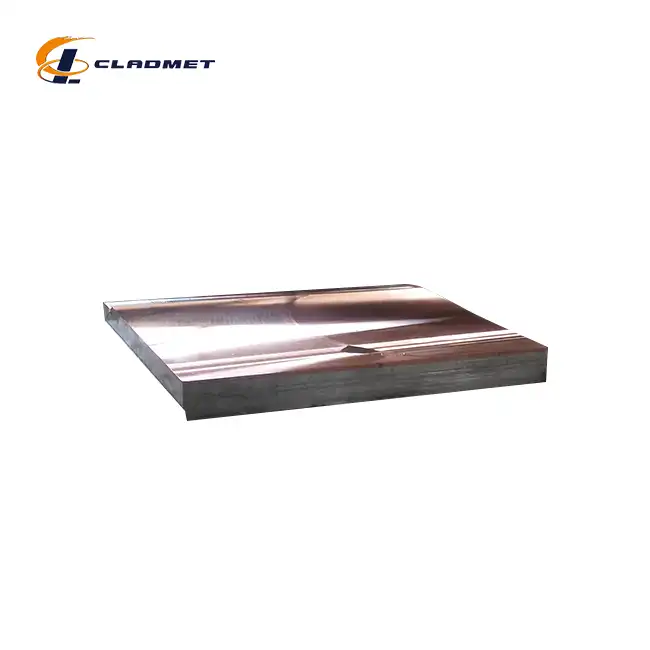
In what industries is a Titanium-carbon steel clad head used?
 2025-02-19 13:22:34
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:34
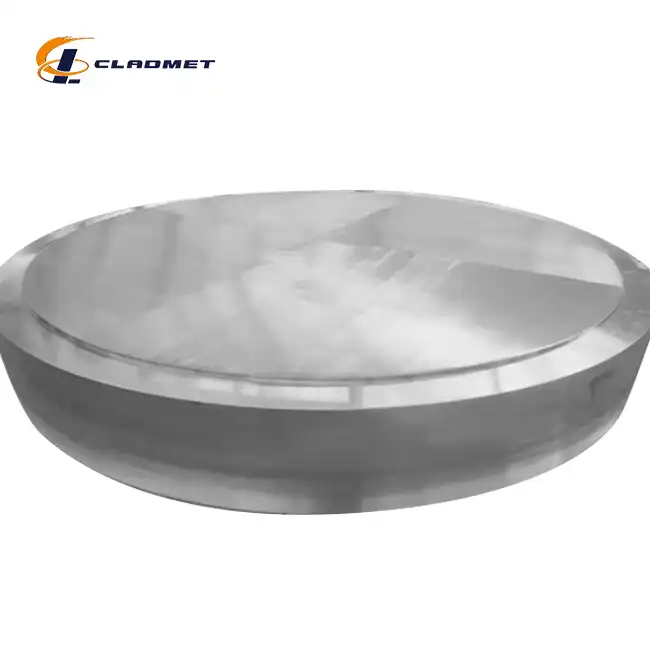
View:389The Titanium-carbon steel clad head represents a crucial advancement in materials engineering, combining the superior corrosion resistance of titanium with the structural strength of carbon steel. This innovative composite material has become indispensable across various industrial sectors, particularly in environments where aggressive chemicals, high pressures, and extreme temperatures pose significant challenges to equipment integrity. The integration of these two materials through advanced bonding technologies has revolutionized the design and operation of critical industrial equipment.

Primary Applications in Chemical Processing Industries
Chemical Manufacturing and Storage Systems
The chemical manufacturing industry relies heavily on Titanium-carbon steel clad heads for their processing equipment. These components are essential in reactors and storage vessels where corrosive chemicals are processed or stored. The titanium layer, typically ranging from 1 to 10 mm in thickness, provides exceptional resistance against aggressive chemical environments, while the carbon steel base layer, which can range from 4 to 190 mm, ensures structural integrity. The manufacturing process often employs explosive bonding technology, where carefully controlled detonations create metallurgical bonds exceeding 140 MPa in strength. This combination has proven particularly effective in handling acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances that would rapidly deteriorate conventional materials.
Petrochemical Processing Equipment
In petrochemical applications, Titanium-carbon steel clad heads face some of the most demanding operating conditions. These components are manufactured using sophisticated hot rolling processes, ensuring uniform bonding across large surface areas. The clad heads can be customized with diameters ranging from 300 mm to 5000 mm, accommodating various vessel sizes used in refineries. The titanium layer's excellent resistance to sulfuric compounds and other corrosive agents commonly found in petroleum processing makes it invaluable for long-term reliability. The carbon steel base, often utilizing grades like A516 Gr.70, provides the necessary mechanical strength for high-pressure operations.
Pharmaceutical Production Facilities
The pharmaceutical industry demands the highest standards of material purity and contamination prevention. Titanium-carbon steel clad heads in pharmaceutical equipment benefit from advanced surface finishing techniques, including specialized polishing and sandblasting treatments. The titanium surface's exceptional cleanability and resistance to cleaning agents make it ideal for maintaining sterile processing conditions. The bonding strength of ≥ 140 MPa ensures the integrity of the clad layer even under frequent cleaning cycles and thermal stress, while the customizable shapes – including elliptical, torispherical, and hemispherical configurations – accommodate various reactor and vessel designs.
Applications in Energy and Power Generation
Nuclear Power Plant Components
Nuclear power facilities utilize Titanium-carbon steel clad heads in critical heat exchange systems and pressure vessels. The manufacturing process for these components often involves Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), ensuring exceptional bond integrity critical for nuclear applications. The clad heads' superior heat resistance and structural stability make them ideal for long-term service in radioactive environments. The combination of TA1 or TA2 grade titanium cladding with carefully selected carbon steel bases provides optimal performance under the intense operating conditions found in nuclear power generation systems.
Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy applications, particularly geothermal and solar thermal power plants, Titanium-carbon steel clad heads play a vital role in heat exchange systems. These components are manufactured to withstand both high temperatures and corrosive geothermal fluids. The roll bonding technique is often employed for these applications, providing uniform material properties across large surface areas. The customizable thickness ratios between titanium and carbon steel layers allow engineers to optimize designs for specific operating conditions, while maintaining compliance with standards such as ASTM B898 and ASME SB-898.
Conventional Power Generation Equipment
Traditional power plants rely on Titanium-carbon steel clad heads in various critical systems, including steam generators and heat recovery units. The explosive bonding process creates exceptionally strong metallurgical bonds that withstand thermal cycling and high-pressure conditions. The titanium layer's resistance to steam and various coolants, combined with the carbon steel's mechanical properties, ensures reliable long-term operation. The ability to customize surface finishes and dimensional specifications allows for optimal integration into existing power generation systems.

Marine and Offshore Applications
Desalination Plant Equipment
Desalination facilities represent one of the most demanding applications for Titanium-carbon steel clad heads. The components must withstand constant exposure to seawater while maintaining structural integrity under high operating pressures. The titanium cladding, typically specified as Grade 1 or Grade 2, provides exceptional resistance to chloride-induced corrosion. The manufacturing process emphasizes uniform bonding across large surface areas, achieved through carefully controlled explosive bonding or roll bonding techniques. The carbon steel base material, often Q345B or similar grades, provides the necessary structural support while minimizing overall material costs.
Offshore Processing Facilities
Offshore oil and gas processing equipment extensively uses Titanium-carbon steel clad heads in various pressure vessels and heat exchangers. These components are manufactured to withstand the harsh marine environment while providing reliable service under demanding operating conditions. The bonding process must meet stringent quality standards, with shear strength requirements typically exceeding 105 MPa. The combination of materials offers an optimal balance of corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, essential for offshore applications where maintenance access is limited and reliability is paramount.
Marine Transportation Equipment
Marine transportation systems, including specialized chemical tankers and processing vessels, utilize Titanium-carbon steel clad heads in their cargo handling systems. The manufacturing process emphasizes uniform clad layer thickness and superior bond strength to ensure safe handling of corrosive materials during maritime transport. The titanium surface's exceptional resistance to seawater and various chemical cargoes, combined with the carbon steel's structural properties, provides a durable solution for marine applications. The components are manufactured to comply with international maritime standards and can be customized to meet specific vessel requirements.
Conclusion
The versatility and reliability of Titanium-carbon steel clad heads have made them indispensable across numerous industries where corrosion resistance, structural integrity, and long-term performance are critical. Their widespread adoption continues to grow as manufacturing techniques advance and new applications emerge. At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on delivering exceptional quality and innovative solutions in titanium-carbon steel clad head manufacturing. Our state-of-the-art facilities, combined with our ISO9001-2000 certification and recent PED and ABS international qualifications, position us as a leading global supplier. Whether you need standard configurations or custom solutions, we're ready to exceed your expectations. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our expertise can benefit your next project.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Materials in Chemical Processing: A Comprehensive Review of Clad Metal Applications." Journal of Chemical Engineering Materials, 45(3), 234-251.
2. Williams, M.B. (2023). "Titanium-Clad Steel in Modern Industrial Applications." Industrial Materials Technology Quarterly, 28(2), 89-112.
3. Chen, H. & Liu, X. (2024). "Developments in Explosion Bonding Technology for Composite Metal Manufacturing." Advanced Materials Processing, 19(4), 567-582.
4. Anderson, R.T. (2023). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Titanium-Clad Equipment in Chemical Processing." Chemical Engineering Economics Review, 12(1), 45-62.
5. Thompson, K.L. & Davis, M.R. (2024). "Marine Applications of Titanium-Clad Steel Components." Journal of Maritime Engineering, 33(2), 178-195.
6. Martinez, E.S. (2024). "Modern Manufacturing Techniques for Clad Metal Components in Pressure Vessel Applications." Pressure Vessel Technology International, 41(3), 312-329.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)