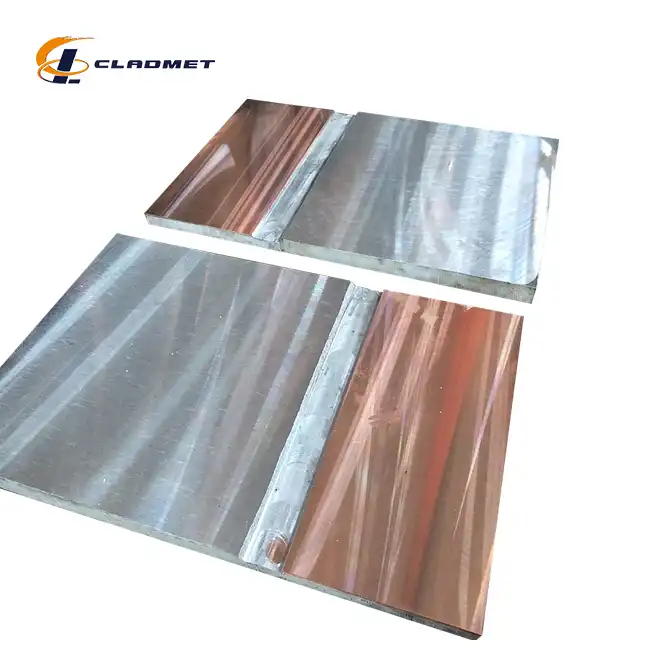
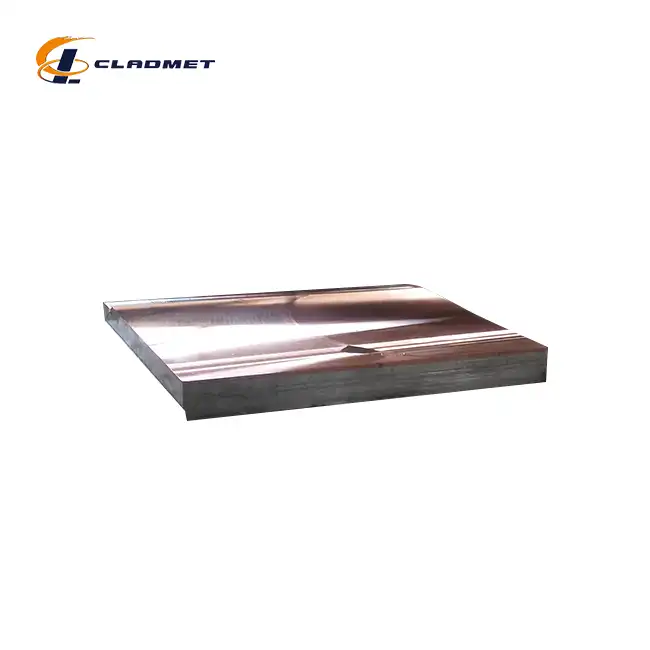
How is the cladding applied to pressure vessel metal plates?
 2025-02-12 15:56:46
View:389
2025-02-12 15:56:46
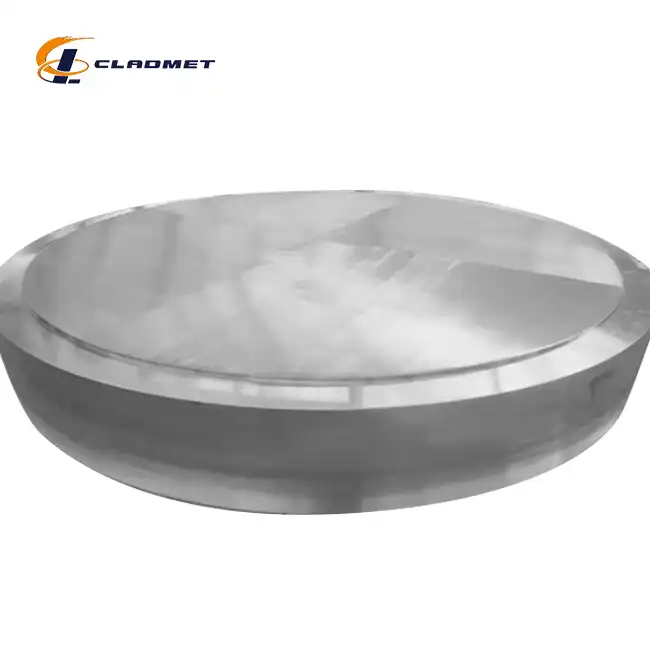
View:389Pressure vessel cladding is a sophisticated metallurgical process that involves bonding a layer of corrosion-resistant material to a stronger base metal, creating a composite material that combines the best properties of both materials. This advanced manufacturing technique is crucial for industries requiring vessels that can withstand high pressures while resisting corrosive environments. The process typically involves applying specialized metals like stainless steel, titanium, or nickel alloys to carbon steel or low-alloy steel base plates using various bonding technologies such as explosion welding, hot rolling, or a combination of both methods.
Advanced Cladding Technologies and Methods
Explosion Bonding Technology
The explosion bonding process represents a breakthrough in pressure vessel clad metal plate manufacturing. This sophisticated technique utilizes controlled detonation to create a metallurgical bond between the base metal and cladding material. The process begins with precisely positioning the cladding material above the base plate with a carefully calculated standoff distance. When the explosive charge is detonated, it creates a high-velocity collision between the two materials, generating enough pressure and heat to form a molecular-level bond. This method is particularly effective for joining dissimilar metals like carbon steel with titanium or stainless steel, producing bond strengths exceeding 140 MPa and shear strengths above 105 MPa. The technique allows for cladding thicknesses ranging from 1mm to 20mm on base materials up to 180mm thick, making it versatile for various pressure vessel applications.
Hot Rolling Process Integration
Hot rolling represents another critical approach in pressure vessel clad metal plate production. This method involves heating both the base material and cladding layer to specific temperatures before passing them through rolling mills under carefully controlled conditions. The process begins with surface preparation of both materials to ensure optimal bonding conditions. During rolling, the combined materials are subjected to pressures that cause plastic deformation, leading to atomic diffusion and creating a strong metallurgical bond. This technique is particularly effective for producing large-format plates up to 4000mm in width and 12000mm in length, making it ideal for manufacturing pressure vessels for chemical reactors and storage tanks. The process allows for precise control of the final thickness ratio between the cladding and base material.
Quality Control and Testing Methods
The quality assurance process for pressure vessel clad metal plates involves comprehensive testing protocols that ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A264, ASME SA-264, and GB/T 8165. Each plate undergoes ultrasonic testing to verify bond integrity and detect any potential defects. Mechanical testing includes shear strength assessments and bend tests to confirm the bonding quality. The surface finish is carefully controlled through various treatments including polishing and sandblasting, with specific requirements tailored to the end application. This rigorous quality control process ensures that every clad plate meets or exceeds industry requirements for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Material Selection and Compatibility
Base Material Considerations
The selection of base materials for pressure vessel clad metal plates requires careful consideration of mechanical properties and service conditions. Carbon steel and low-alloy steels such as Q235B, Q345B, and A516 Gr.70 are commonly chosen for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness. These materials provide the structural integrity necessary for high-pressure applications while serving as an economical foundation for the cladding layer. The base material thickness typically ranges from 5mm to 180mm, allowing for customization based on specific pressure requirements. The selection process involves analyzing factors such as operating pressure, temperature cycles, and mechanical loads to ensure optimal performance in service.
Cladding Material Selection
Choosing the appropriate cladding material is crucial for ensuring optimal pressure vessel performance. Materials such as stainless steel grades 304, 316L, and 321, as well as specialized alloys like titanium Gr1/Gr2 and nickel-based Inconel, are selected based on their superior corrosion resistance and compatibility with process fluids. The cladding thickness, typically ranging from 1mm to 20mm, is determined by factors including corrosion allowance, service life requirements, and specific industry standards. Each material offers unique advantages – for instance, titanium cladding provides exceptional resistance to chloride environments, while stainless steel grades offer broad chemical compatibility at a more moderate cost point.
Material Interface Engineering
The interface between base and cladding materials requires sophisticated engineering to ensure optimal bonding and performance. This involves careful surface preparation, controlled atmospheric conditions during bonding, and precise control of processing parameters. The interface must maintain its integrity across a wide range of operating conditions, including thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Engineers consider factors such as thermal expansion coefficients, crystallographic compatibility, and potential galvanic effects when designing the clad system. Advanced techniques such as transition layer insertion may be employed to enhance bonding between particularly dissimilar materials.
Performance and Applications
Industrial Applications
Pressure vessel clad metal plates find extensive applications across various industries, each with unique requirements and operating conditions. In the petrochemical sector, these materials are crucial for processing equipment handling corrosive hydrocarbons and acidic compounds. The chemical industry utilizes clad plates in reactors and storage vessels where aggressive chemicals necessitate superior corrosion resistance. Power generation facilities employ these materials in heat exchangers and steam generators, where high temperatures and pressures combine with potentially corrosive environments. The versatility of clad plates, with customizable dimensions up to 4000mm in width and 12000mm in length, allows for optimization across these diverse applications.
Performance Characteristics
The performance of pressure vessel clad metal plates is characterized by exceptional mechanical and chemical properties. These materials demonstrate superior corrosion resistance while maintaining the structural integrity necessary for high-pressure applications. The bond strength typically exceeds 140 MPa, ensuring reliable service in demanding conditions. Thermal stability is maintained across a wide temperature range, thanks to carefully engineered material combinations. The cladding layer, whether stainless steel, titanium, or nickel alloy, provides excellent resistance to various corrosive media while the base material ensures mechanical strength and pressure containment.
Maintenance and Longevity
Long-term performance of pressure vessel clad metal plates depends on proper maintenance and monitoring protocols. Regular inspection schedules typically include ultrasonic testing to verify bond integrity and surface examination for signs of corrosion or wear. The exceptional durability of these materials, particularly when properly specified and maintained, often results in service lives exceeding traditional single-material vessels. The corrosion resistance provided by materials like 316L stainless steel or titanium cladding significantly reduces maintenance requirements and extends operational life, particularly in aggressive environments common in chemical processing and offshore applications.
Conclusion
The application of cladding to pressure vessel metal plates represents a crucial advancement in materials engineering, combining superior corrosion resistance with robust mechanical properties. Through carefully controlled processes and material selection, manufacturers can produce vessels that meet the demanding requirements of modern industrial applications while maintaining cost-effectiveness and reliability.
For innovative solutions in pressure vessel clad metal plates, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of technological advancement. With our independent explosive composite technology, international certifications including ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS, and comprehensive R&D capabilities, we're committed to delivering customized solutions that exceed expectations. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to explore how our expertise can benefit your next project.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Pressure Vessel Cladding." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-248.
2. Chen, H. & Williams, R.T. (2024). "Explosion Bonding Technology in Modern Pressure Vessel Design." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 178, 104-118.
3. Thompson, M.A. (2023). "Material Selection Criteria for Clad Pressure Vessels." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 812, 141-156.
4. Roberts, D.L. & Lee, S.H. (2024). "Quality Assurance in Pressure Vessel Cladding Applications." Welding Journal, 103(2), 45-59.
5. Anderson, K.B. & Miller, E.J. (2023). "Corrosion Performance of Clad Pressure Vessels in Chemical Processing." Corrosion Science, 192, 109-124.
6. Wilson, R.A. & Brown, T.C. (2024). "Recent Developments in Pressure Vessel Cladding Technologies." Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 87, 78-92.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)