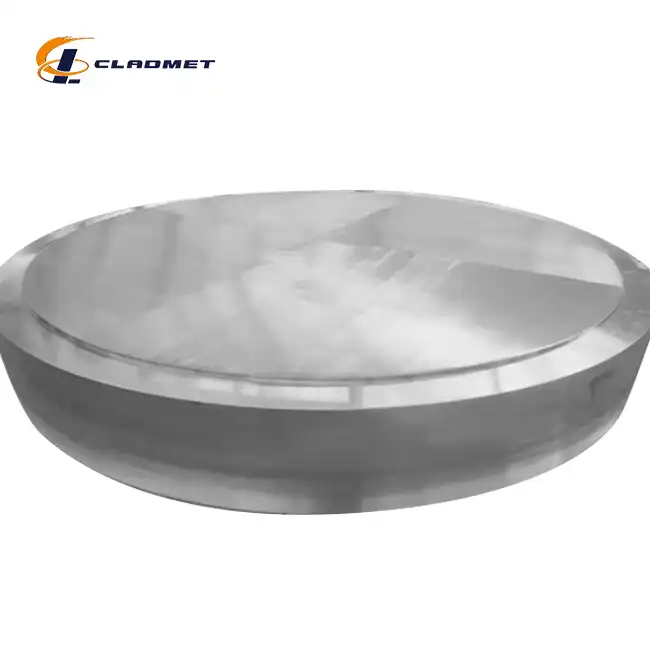
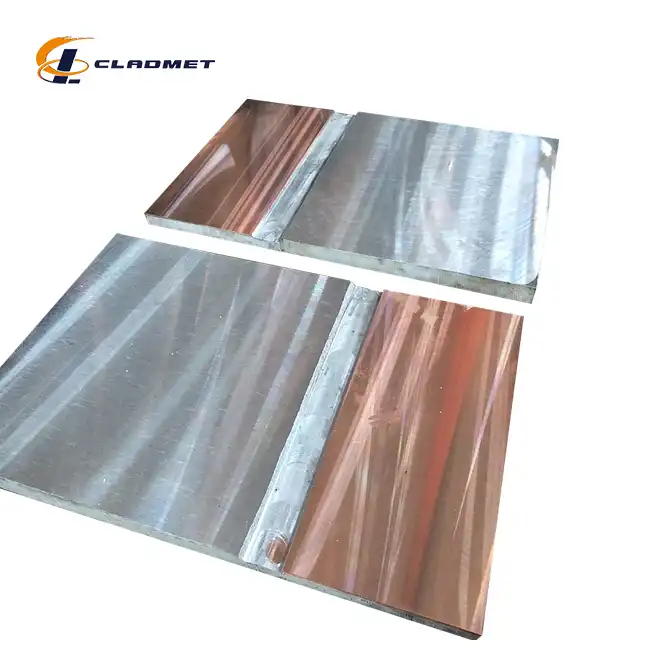
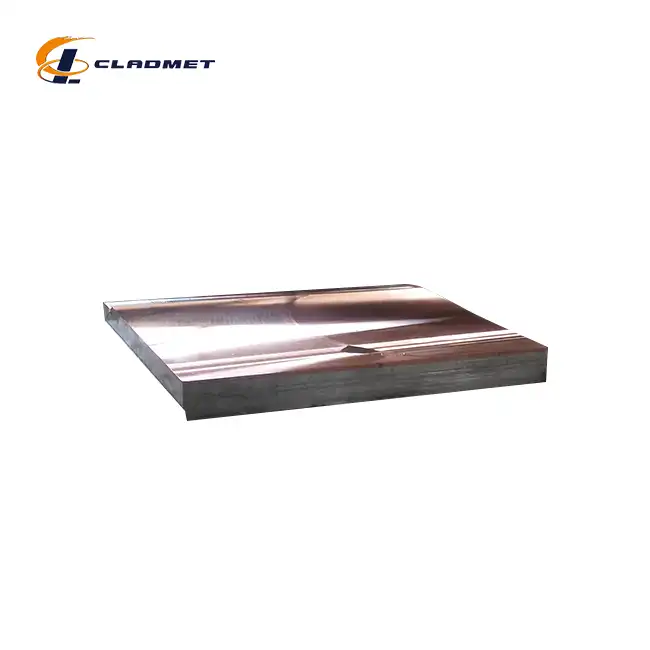
How are Clad Tube Plates Manufactured?
 2025-04-27 11:29:54
View:389
2025-04-27 11:29:54
View:389Clad tube plates represent a cornerstone innovation in industrial materials engineering, combining multiple metal layers to create components with superior performance characteristics. These specialized plates are essential for heat exchangers, pressure vessels, and chemical processing equipment where single metals alone cannot withstand extreme operating conditions. The manufacturing process of clad tube plates involves sophisticated metallurgical techniques that permanently bond dissimilar metals, creating a composite material that leverages the strengths of each component while minimizing weaknesses. This article explores the intricate manufacturing methods, quality control processes, and industrial applications that make clad tube plates indispensable in modern engineering solutions.
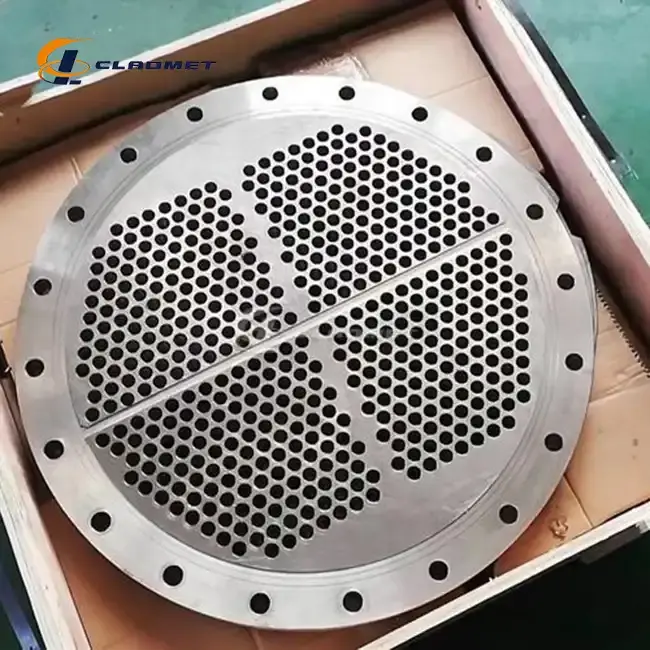

Advanced Manufacturing Processes for Clad Tube Plates
Explosive Bonding Technology
Explosive bonding stands as one of the most effective and widely used methods in clad tube plate manufacturing at facilities like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. This sophisticated process creates an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond between dissimilar metals through controlled detonation. During explosive bonding, technicians position the base metal (typically carbon or stainless steel) and the cladding material (such as titanium, nickel alloy, or other corrosion-resistant metals) in a precise arrangement. A carefully calculated explosive charge is then detonated above the plates, creating a high-velocity collision between the metals. This collision generates intense localized pressure and heat at the interface, resulting in atomic-level bonding without melting the materials. The wave-like interface characteristic of explosive bonding creates a mechanical interlock that significantly enhances bond strength compared to other methods. This manufacturing technique is particularly valuable for clad tube plates destined for harsh environments, such as those in petrochemical facilities, offshore platforms, and chemical processing plants. Baoji JL Clad Metals has refined this explosive composite technology to achieve bond integrity that consistently meets or exceeds international standards, including ASME, ASTM, and JIS specifications. The explosive bonding technique allows for the creation of clad tube plates with customizable dimensions, with capabilities for plates up to 6 meters in length and 3 meters in width, making them suitable for large-scale industrial applications.
Roll Bonding Process
Roll bonding represents another critical manufacturing approach in the production of high-quality clad tube plates. This process involves preparing the surfaces of both the base metal and the cladding material through meticulous cleaning and surface treatment to remove oxides and contaminants that could compromise bond integrity. The metals are then stacked together and heated to temperatures below their melting points but high enough to induce plasticity. The heated metal sandwich passes through powerful rolling mills where tremendous pressure forces the materials together, creating a solid-state diffusion bond at the interface. Multiple rolling passes may be required to achieve the desired reduction in thickness and ensure complete bonding across the entire surface area of the clad tube plate. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. employs advanced self-rolling plate technology that allows for precise control over the rolling parameters, resulting in consistent bond quality and superior mechanical properties. This method is particularly advantageous for producing clad tube plates with uniform thickness and excellent surface finish, critical factors for applications in heat exchangers where thermal efficiency depends on surface characteristics. Roll-bonded clad tube plates can be manufactured with thicknesses ranging from 5mm to 100mm, accommodating diverse industrial requirements. The controlled nature of the roll bonding process makes it ideal for producing clad tube plates that require predictable mechanical properties and dimensional stability across large surface areas.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing represents a cutting-edge manufacturing technique in the clad tube plate industry, particularly suited for applications requiring exceptional bond quality and uniformity. The HIP process begins with carefully preparing and assembling the base metal and cladding material components in a vacuum-sealed container. This assembly is then subjected to simultaneous high pressure (typically 100-200 MPa) and elevated temperatures (often 900-1200°C) in a specialized pressure vessel. The combination of heat and isostatic (equal from all directions) pressure facilitates atomic diffusion across the interface, creating a metallurgical bond without the wave pattern characteristic of explosive bonding. At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., this advanced technique enables the production of premium clad tube plates with virtually defect-free bonds, crucial for critical applications in pharmaceutical reactors, nuclear components, and aerospace systems. The controlled environment of the HIP process prevents oxidation and contamination, resulting in clad tube plates with superior corrosion resistance and mechanical integrity. This manufacturing method allows for the combination of exotic metals that might be challenging to bond through other techniques, expanding the range of available material combinations to include specialized pairings such as titanium-steel, zirconium-steel, and tantalum-steel clad tube plates. While generally more expensive than other methods, HIP produces clad tube plates with exceptional reliability and performance characteristics, making it the preferred option for high-stakes applications where failure is not an option.
Quality Control and Material Selection in Clad Tube Plate Production
Non-Destructive Testing Methods
The quality and reliability of clad tube plates depend heavily on rigorous non-destructive testing protocols implemented throughout the manufacturing process. At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., comprehensive testing regimes ensure that every clad tube plate meets or exceeds industry standards before deployment in critical applications. Ultrasonic testing represents the cornerstone of quality assurance for clad tube plates, as it can detect delamination, voids, or incomplete bonding at the interface between the base metal and cladding material. During this process, high-frequency sound waves are transmitted through the clad tube plate, and any discontinuities in the bond interface reflect these waves, allowing technicians to create detailed maps of bond integrity across the entire surface. Radiographic examination provides another layer of verification, using X-rays or gamma rays to penetrate the clad tube plate and identify internal defects that might compromise performance. For surface-critical applications, dye penetrant testing and magnetic particle inspection are employed to detect surface and near-surface flaws in the clad tube plate that could serve as initiation points for corrosion or mechanical failure. These non-destructive testing methods work in concert to ensure that every clad tube plate delivers consistent performance throughout its service life, particularly important for applications in pressure vessels and heat exchangers where failure could result in catastrophic consequences. Baoji JL's commitment to quality is evidenced by their successful certification under ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS international qualifications, confirming adherence to the stringent quality control standards that modern industrial applications demand.
Material Combination Engineering
The strategic selection and engineering of material combinations form the foundation of effective clad tube plate design and manufacturing. Engineers at Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. carefully analyze the intended operating environment and performance requirements to determine the optimal pairing of base metal and cladding material for each application. The base metal, typically carbon steel or stainless steel, provides the structural strength and cost-effectiveness that make clad tube plates economically viable for large-scale industrial use. Meanwhile, the cladding material—which might include titanium, nickel alloys, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, tantalum, zirconium, or columbium—delivers the specialized surface properties required for specific operating conditions. For applications involving highly corrosive media, titanium or nickel-based superalloys serve as the cladding material of choice due to their exceptional resistance to chemical attack. In contrast, copper cladding might be selected for applications requiring enhanced thermal conductivity in heat exchanger tube plates. The thickness ratio between the base metal and cladding material requires careful optimization to balance performance requirements with economic considerations, typically ranging from 5% to 20% of the total thickness for the cladding layer. Baoji JL offers customizable specifications according to client requirements, with clad tube plates available in thicknesses from 5mm to 100mm, lengths up to 6 meters, and widths up to 3 meters. This tailored approach to material combination engineering ensures that each clad tube plate delivers optimal performance in its intended application, whether in petroleum refineries, chemical processing facilities, pharmaceutical manufacturing plants, or power generation systems.
Surface Treatment and Finishing
The final surface treatment and finishing processes applied to clad tube plates significantly influence their performance, longevity, and aesthetic qualities in industrial applications. After the primary manufacturing process—whether explosive bonding, roll bonding, or hot isostatic pressing—clad tube plates undergo meticulous surface preparation to enhance their functional characteristics. At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., a diverse range of surface treatments is available to meet specific client requirements and application demands. Mechanical polishing creates a smooth, uniform surface on clad tube plates destined for heat exchangers and pharmaceutical equipment, where cleanability and minimal flow resistance are paramount. For enhanced corrosion protection, especially in marine and chemical processing environments, clad tube plates may receive specialized anti-corrosion coatings that extend service life and maintain integrity under harsh conditions. Sandblasting offers an alternative surface preparation method that creates a textured finish with increased surface area, beneficial for applications requiring enhanced heat transfer efficiency or improved adhesion for subsequent coatings. Edge preparation represents another critical aspect of finishing, as the transition between the cladding material and base metal at the edges of clad tube plates can be vulnerable to corrosion and mechanical damage if not properly protected. Various edge treatment methods, including seal welding and specialized coatings, ensure comprehensive protection across the entire clad tube plate. For clients with specific visual or functional requirements, Baoji JL offers customized surface finishes including patterned surfaces, specialized roughness profiles, and color-coded markings for identification and traceability. These finishing processes not only enhance the performance characteristics of clad tube plates but also ensure they meet the aesthetic and functional standards expected in premium industrial components.
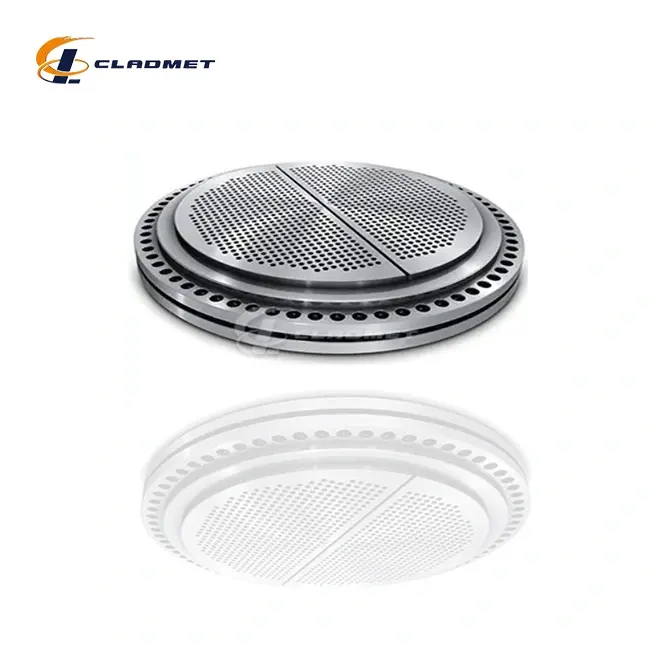

Industrial Applications and Performance Characteristics
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing Equipment
The harsh operating conditions encountered in chemical and petrochemical processing facilities demand materials that can withstand aggressive chemical environments while maintaining structural integrity—requirements that make clad tube plates indispensable in this sector. Within distillation columns, reactors, and separation vessels, clad tube plates function as critical components exposed to corrosive chemicals, high temperatures, and substantial mechanical stress. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. produces specialized clad tube plates for these applications, typically utilizing stainless steel or nickel alloy cladding on carbon steel base plates to achieve the optimal balance between corrosion resistance and structural strength. In petrochemical refineries, where hydrocarbon processing involves exposure to sulfur compounds and organic acids, titanium-clad tube plates provide exceptional resistance to sulfidation corrosion while the steel substrate delivers the necessary mechanical support at significantly lower cost than solid titanium construction. Pharmaceutical manufacturing presents another demanding application, where ultra-pure production environments require clad tube plates with exceptional surface quality and resistance to cleaning chemicals; here, polished stainless steel cladding on carbon steel base plates offers an ideal solution. The dimensional stability of clad tube plates under thermal cycling conditions makes them particularly valuable in batch processing equipment where temperature fluctuations are common. Baoji JL offers customized clad tube plates ranging from 5mm to 100mm in thickness, with lengths up to 6 meters and widths up to 3 meters, accommodating the scale requirements of industrial chemical processing equipment. Each clad tube plate undergoes rigorous quality control, including non-destructive testing and mechanical property verification, ensuring reliable performance in these mission-critical applications where equipment failure could lead to production losses, environmental incidents, or safety hazards.
Heat Exchanger Tube Sheets
Heat exchangers represent one of the most widespread and demanding applications for clad tube plates, where they function as tube sheets that secure and separate the many tubes through which heat transfer occurs. In these systems, clad tube plates must simultaneously withstand corrosive process fluids, substantial temperature differentials, and significant mechanical loads from internal pressure and thermal expansion. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures specialized clad tube plates for heat exchanger applications with precisely drilled hole patterns to accommodate tube insertion, with capabilities for creating complex configurations involving hundreds or even thousands of precisely positioned holes. The strategic advantage of using clad tube plates in heat exchangers lies in their ability to present corrosion-resistant surfaces to process fluids while maintaining structural integrity through the economical base metal. In seawater-cooled condensers for power generation facilities, titanium-clad tube plates resist the aggressive chloride corrosion that would rapidly degrade conventional materials, while the steel substrate provides the necessary strength at a fraction of the cost of solid titanium construction. For chemical processing heat exchangers handling acidic or caustic fluids, stainless steel or nickel alloy cladding on carbon steel tube sheets delivers optimal performance characteristics. The thermal conductivity of the clad tube plate also influences heat exchanger efficiency, particularly at the tube-to-tubesheet junction where heat transfer occurs across multiple material interfaces. Baoji JL's advanced roll bonding and explosive welding techniques create metallurgical bonds with minimal thermal resistance, enhancing overall heat exchanger performance. Additionally, the company offers customization options including specialized surface treatments, precise dimensional tolerances, and material combinations tailored to specific heat transfer requirements. These high-performance clad tube plates maintain their integrity through countless thermal cycles and pressure fluctuations, making them the preferred choice for critical heat exchange applications in industries ranging from power generation to chemical processing, food production, and HVAC systems.
Pressure Vessels and Storage Tanks
In pressure vessels and storage tanks designed for containing hazardous or valuable materials under pressure, clad tube plates play a pivotal role in ensuring operational safety, reliability, and longevity. These specialized components form the critical junctions where piping systems connect to vessels, where inspection ports are located, and where internal components attach to the vessel structure. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. produces custom-engineered clad tube plates for these applications with material combinations specifically selected to address the unique challenges of each operating environment. For cryogenic storage vessels containing liquefied natural gas or other refrigerated gases, stainless steel-clad tube plates provide the necessary low-temperature toughness at the process fluid interface while the carbon steel base delivers economical structural support. In high-pressure reactors operating at elevated temperatures, such as those found in hydrocracking units in petroleum refineries, nickel alloy-clad tube plates resist both hydrogen embrittlement and high-temperature oxidation while maintaining mechanical integrity. Chlor-alkali production facilities utilize titanium-clad tube plates to withstand the extremely corrosive chlorine environment while reducing construction costs compared to solid titanium alternatives. The substantial thickness range available from Baoji JL (5mm to 100mm) accommodates the varying pressure ratings required in different vessel applications, while sizes up to 6 meters in length and 3 meters in width allow for the construction of industrial-scale equipment. Each clad tube plate undergoes comprehensive testing including ultrasonic inspection, radiographic examination, and mechanical property verification to ensure compliance with international standards such as ASME, ASTM, and JIS. The successful certification under PED and ABS standards further validates the suitability of these components for pressure-containing applications where safety is paramount. Through careful material selection, precise manufacturing, and rigorous quality control, Baoji JL's clad tube plates provide the performance characteristics necessary for pressure vessels and storage tanks operating in the most demanding industrial environments, from offshore platforms to chemical processing facilities and beyond.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of clad tube plates represents a sophisticated metallurgical process that delivers exceptional performance in demanding industrial applications. Through advanced techniques like explosive bonding, roll bonding, and hot isostatic pressing, manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. create composite materials that combine the best properties of different metals to withstand extreme conditions while offering economic advantages over solid exotic metals. Ready to elevate your project with premium-quality clad tube plates? At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we bring together independent explosive composite technology, self-rolling capabilities, and international certifications to deliver superior products tailored to your specifications. Our R&D team specializes in innovative design solutions that address your unique challenges, while our OEM/ODM services ensure you receive exactly what your application demands. Experience the difference that comes with ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS certified manufacturing excellence. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our advanced clad tube plates can enhance your industrial operations and deliver lasting value.
References
1. Zhang, L., & Wang, C. (2023). Advances in Explosive Bonding Techniques for Industrial Clad Metal Production. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 301, 117-134.
2. Robertson, I. M., & Schaffer, G. B. (2022). Metallurgical Bonding Mechanisms in Clad Tube Plate Manufacturing. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 845, 142-157.
3. Findik, F., & Yilmaz, R. (2023). A Comprehensive Review of Roll Bonding for Bimetallic Composite Materials. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 115, 1247-1268.
4. Alhawari, K. S., & Jawad, Z. A. (2022). Quality Assurance Methods for Clad Tube Plates in Heat Exchanger Applications. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 31(4), 2873-2889.
5. Chen, S., & Li, D. (2024). Hot Isostatic Pressing: Principles and Applications in Clad Metal Manufacturing. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(1), 127-145.
6. Park, H., & Johnson, T. (2023). Industrial Applications of Clad Tube Plates: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Materials & Design, 226, 211-228.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)