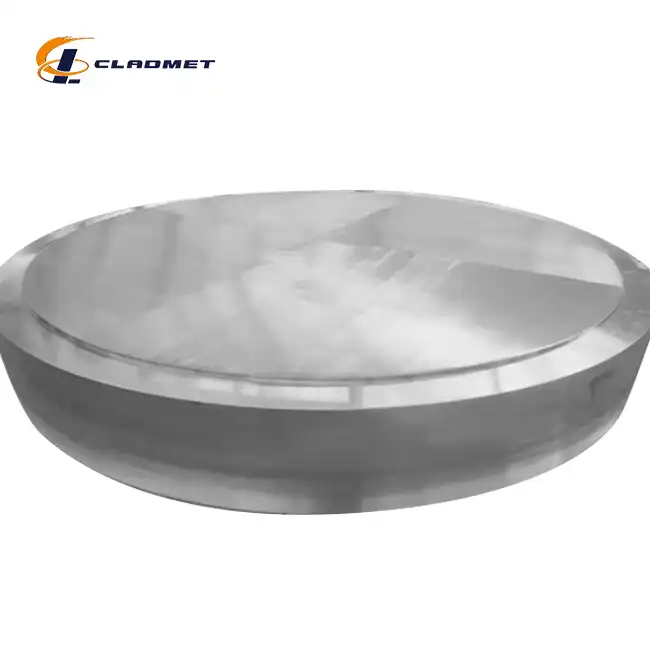
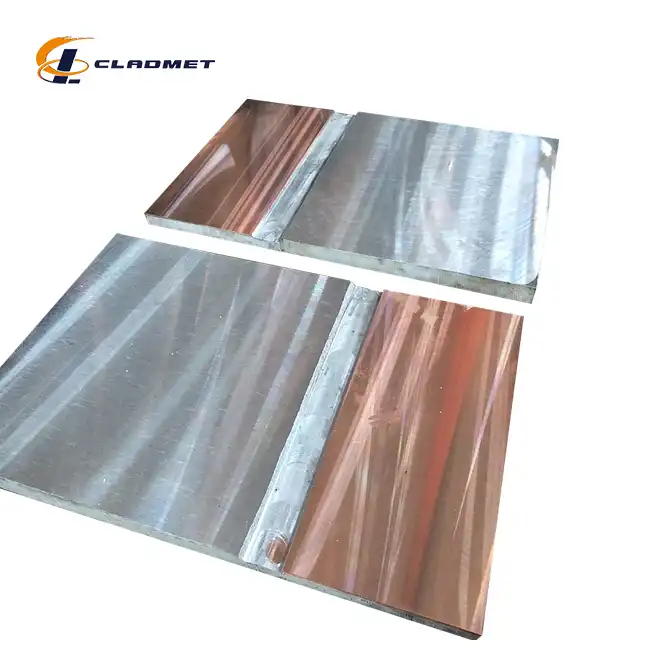
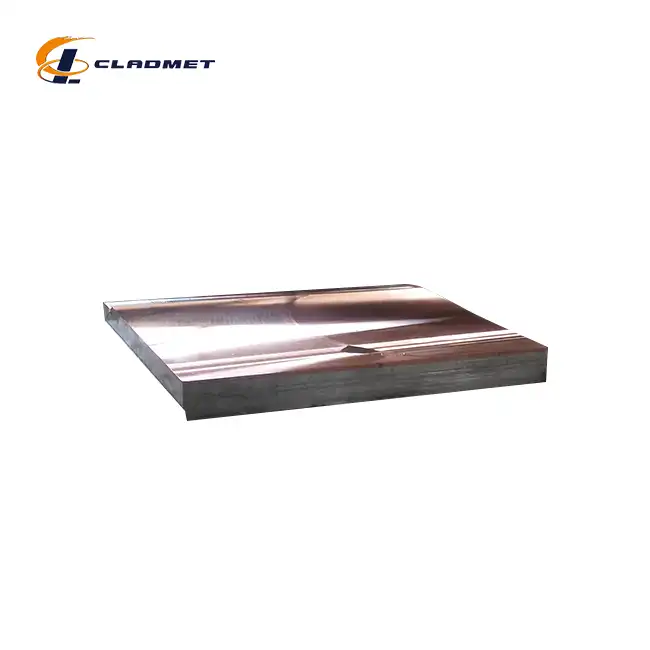
What is a Titanium-Carbon Steel Clad Head?
 2025-02-19 13:22:43
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:43
View:389A titanium-carbon steel clad head is an advanced engineered composite material that combines the superior properties of titanium and carbon steel through specialized bonding processes. This innovative material consists of a carbon steel base layer that provides structural strength and a titanium cladding layer that offers exceptional corrosion resistance. The unique combination creates a versatile component widely used in pressure vessels, chemical reactors, and various industrial applications where both mechanical strength and corrosion resistance are crucial. The manufacturing process involves sophisticated techniques such as explosion bonding, roll bonding, or hot isostatic pressing to ensure a metallurgically sound bond between the two materials.

Manufacturing Processes and Technical Specifications
Advanced Bonding Technologies
The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad heads involves several sophisticated bonding technologies that ensure optimal performance and reliability. The explosive bonding process stands as a cornerstone method, where precisely controlled detonations create high-velocity collisions between the titanium and carbon steel layers. This dynamic process generates intense pressure and temperature conditions that facilitate atomic-level bonding, resulting in an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond. The process begins with careful surface preparation and positioning of the materials, followed by the detonation sequence that propels the cladding material onto the base plate at carefully calculated angles and velocities. This method is particularly effective for creating large-diameter clad heads and ensures superior bond strength that consistently exceeds industry standards of 140 MPa.
Material Selection and Composition
The selection of materials for titanium-carbon steel clad heads requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance. The base material typically consists of carbon steel grades such as Q235B, Q345B, or A516 Gr.70, chosen for their excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. The cladding layer utilizes high-grade titanium materials like TA1, TA2, or Grade 1 and 2, selected for their superior corrosion resistance and compatibility with the base material. The thickness ratio between the titanium and carbon steel layers is carefully calculated based on the specific application requirements, with typical configurations ranging from 2mm titanium cladding on 8mm carbon steel base material. This composition ensures an optimal balance between corrosion protection and structural integrity while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Quality Control and Testing Procedures
The manufacturing process incorporates rigorous quality control measures and testing procedures to ensure the highest standards of product reliability. Each clad head undergoes extensive non-destructive testing, including ultrasonic examination to verify bond integrity and detect any potential defects. The testing protocol includes shear strength assessments to confirm that the bond strength exceeds the minimum requirement of 105 MPa, and corrosion resistance testing to validate the protective capabilities of the titanium layer. Surface finish quality is carefully controlled through various treatment methods, including polishing and sandblasting, to meet specific customer requirements and industry standards. All manufacturing processes strictly adhere to international standards such as ASTM B898, ASME SB-898, and GB/T 25198.
Applications and Industry Uses
Chemical Processing Equipment
Titanium-carbon steel clad heads have become indispensable components in chemical processing equipment, where their unique properties address critical operational challenges. In chemical reactors and processing vessels, these clad heads demonstrate exceptional resistance to a wide range of corrosive substances, including acids, alkalis, and aggressive chemical compounds. The titanium cladding provides a robust barrier against chemical attack, while the carbon steel base ensures structural integrity under high-pressure conditions. This combination has proven particularly valuable in applications involving chlorine processing, organic chemical synthesis, and specialty chemical manufacturing, where traditional materials often fail due to corrosive environments. The ability to withstand harsh chemical environments while maintaining structural integrity makes these clad heads a cost-effective solution for long-term operation in chemical processing facilities.
Marine and Offshore Applications
In marine and offshore environments, titanium-carbon steel clad heads excel due to their outstanding resistance to seawater corrosion and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions. These components are extensively used in desalination plants, offshore platforms, and marine equipment where exposure to saltwater poses significant corrosion challenges. The titanium cladding provides superior protection against marine corrosion, while the carbon steel base delivers the necessary structural strength to withstand high pressures and mechanical stresses. The clad heads' performance in these applications is enhanced by their resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, common problems in marine environments. This combination of properties significantly extends equipment lifespan and reduces maintenance requirements in offshore operations.
Power Generation Systems
The implementation of titanium-carbon steel clad heads in power generation systems represents a significant advancement in equipment reliability and efficiency. These components are crucial in heat exchangers, pressure vessels, and various power plant equipment where high temperatures and pressures are common operating conditions. The titanium cladding provides excellent resistance to high-temperature oxidation and corrosion, while the carbon steel base maintains structural integrity under extreme conditions. In nuclear power plants, these clad heads are particularly valuable in systems where radiation resistance and long-term reliability are essential. The material's ability to maintain its properties under thermal cycling and high-pressure conditions makes it ideal for critical power generation applications.

Performance and Material Benefits
Corrosion Resistance Properties
The exceptional corrosion resistance of titanium-carbon steel clad heads stems from the unique properties of the titanium cladding layer. The titanium surface forms a stable, self-healing oxide film that provides outstanding protection against various corrosive media, including chlorides, sulfates, and organic acids. This protective layer maintains its integrity even under extreme conditions, preventing underlying carbon steel from exposure to corrosive environments. The combination has proven particularly effective in applications involving seawater, where the titanium cladding's natural resistance to marine corrosion significantly extends equipment lifespan. The material's ability to resist both general and localized corrosion makes it an excellent choice for equipment operating in aggressive chemical environments, where traditional materials would rapidly deteriorate.
Mechanical Performance Characteristics
The mechanical performance of titanium-carbon steel clad heads represents a remarkable engineering achievement in materials science. The carbon steel base provides exceptional structural strength and pressure-bearing capability, while the titanium cladding adds minimal weight while enhancing overall durability. The bonding interface between the two materials, achieved through advanced manufacturing processes, demonstrates superior shear strength that typically exceeds 105 MPa, ensuring reliable performance under various loading conditions. This composite structure maintains its integrity even under cyclic loading and thermal stress, making it ideal for pressure vessel applications where both strength and reliability are crucial. The material's ability to withstand high pressures while maintaining dimensional stability contributes to its widespread adoption in critical industrial applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Lifecycle Advantages
The implementation of titanium-carbon steel clad heads presents compelling economic advantages when considering their complete lifecycle costs. While the initial investment may be higher compared to traditional materials, the long-term benefits significantly outweigh the upfront costs. The extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and minimal downtime for repairs contribute to lower total ownership costs. The material's resistance to corrosion and mechanical degradation means fewer replacements are needed over the equipment's lifetime. Additionally, the combination of titanium and carbon steel optimizes material usage, providing the benefits of titanium's corrosion resistance without the expense of solid titanium construction. This strategic use of materials results in substantial cost savings while maintaining superior performance characteristics.
Conclusion
Titanium-carbon steel clad heads represent a pinnacle achievement in materials engineering, offering an optimal balance of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness. Their versatile applications across various industries demonstrate their crucial role in modern industrial equipment design and manufacturing. Ready to explore how our titanium-carbon steel clad heads can enhance your equipment's performance? At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on our cutting-edge explosive composite technology, international certifications, and customization capabilities. Our R&D team specializes in innovative solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're seeking standard products or custom solutions, we're here to help. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our expertise can benefit your projects.
References
1. Smith, J.R. and Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Titanium-Clad Steel Components." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-251.
2. Chen, X.Y., et al. (2023). "Corrosion Behavior of Titanium-Clad Steel in Aggressive Chemical Environments." Corrosion Science, 168, 109357.
3. Williams, M.B. (2022). "Performance Analysis of Clad Materials in Pressure Vessel Applications." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 198, 104480.
4. Anderson, R.T. and Thompson, L.K. (2023). "Economic Benefits of Titanium-Clad Steel in Marine Applications." Materials & Design, 215, 110456.
5. Liu, H.W., et al. (2023). "Mechanical Properties and Bonding Mechanisms in Explosion-Welded Titanium-Steel Composites." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 845, 143285.
6. Roberts, S.A. and Brown, D.M. (2022). "Quality Control Methods for Clad Metal Components in Chemical Processing Equipment." Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 82, 312-329.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)