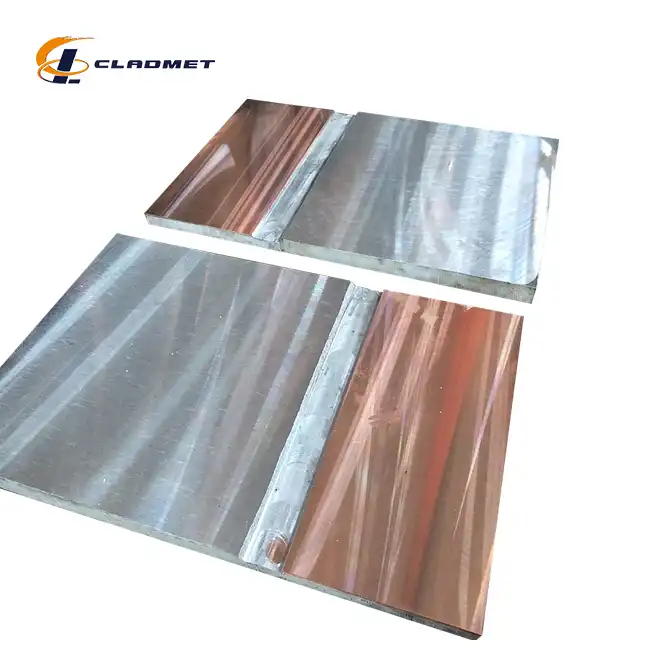
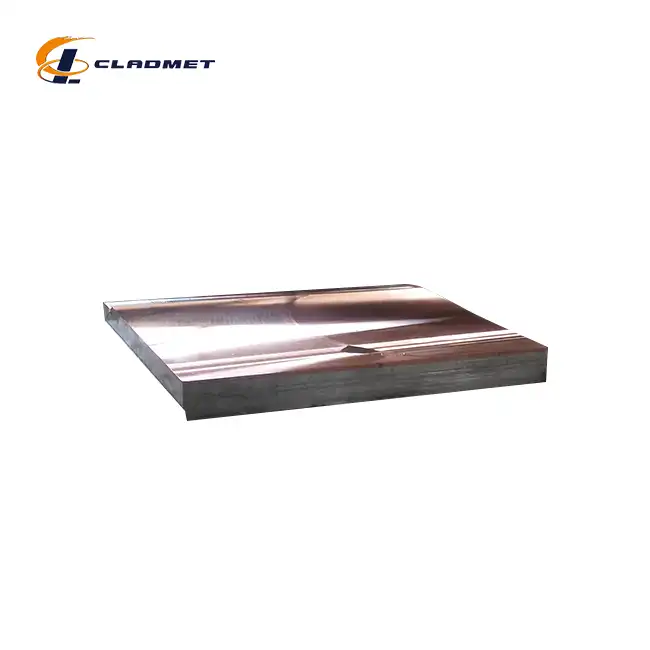
What Industries Use Titanium Clad Steel Plates?
 2025-03-05 10:10:26
View:389
2025-03-05 10:10:26
View:389Titanium Clad Steel Plates represent one of the most versatile and robust composite materials in modern industrial applications. These innovative materials combine the exceptional corrosion resistance of titanium with the structural strength and cost-effectiveness of steel, creating a superior solution for demanding environments. As industries face increasingly challenging operational conditions and stringent safety requirements, Titanium Clad Steel Plates have emerged as a critical component across multiple sectors. This article explores the diverse industries leveraging these remarkable composite materials and examines their specific applications, benefits, and technological developments.

Key Industries Utilizing Titanium Clad Steel Plates
Titanium Clad Steel Plates have revolutionized material selection across multiple high-demand industries due to their exceptional performance characteristics. These composite materials, ranging from 3mm to 200mm in thickness and up to 12,000mm in length, provide an optimal balance between durability and functionality.
Chemical Processing Industry
The chemical processing industry relies heavily on Titanium Clad Steel Plates for handling aggressive chemicals and maintaining operational integrity. These plates feature titanium layers bonded to carbon or stainless steel bases using advanced explosion bonding or roll bonding technologies that create an unbreakable metallurgical bond. In acid production facilities, the titanium layer's exceptional resistance to chlorides, sulfates, and other corrosive compounds protects the underlying steel structure, extending equipment lifespan significantly. Chemical manufacturers particularly value these plates for reactor vessels where high-temperature operations occur simultaneously with exposure to corrosive media. The customizable dimensions—with widths up to 3,000mm—allow fabricators to design pressure vessels that maintain structural integrity while minimizing material costs compared to solid titanium construction. Additionally, the polished, sandblasted, or acid-pickled surface treatments available for these plates ensure optimal performance in specific chemical environments.
Oil and Gas Exploration
The petroleum industry faces some of the most challenging material requirements, making Titanium Clad Steel Plates indispensable components in their operations. Offshore platforms and refineries utilize these composite materials extensively in equipment exposed to seawater, crude oil, and processing chemicals. Titanium Clad Steel Plates excel in these environments due to their remarkable resistance to galvanic corrosion and chloride attack—problems that conventional materials struggle to withstand. Desalination units in oil production facilities benefit from the titanium layer's immunity to saltwater corrosion while drawing structural support from the steel base. The plates' thickness range of 3mm to 200mm provides engineers with flexibility when designing equipment for various pressure ratings. Furthermore, these plates maintain their integrity during the thermal cycling common in refinery operations, where temperatures fluctuate extensively. The explosion-bonded Titanium Clad Steel Plates also demonstrate superior performance at the critical pipe-to-vessel connections where stress concentration and corrosion risks are highest.
Marine Engineering Applications
Maritime environments present unique challenges that Titanium Clad Steel Plates address effectively. Shipbuilding and offshore structure construction rely on these materials for components exposed to constant seawater contact. The titanium layer provides exceptional protection against marine biofouling and galvanic corrosion—persistent problems in ocean environments. Naval vessels employ Titanium Clad Steel Plates in condensers, heat exchangers, and desalination equipment where the material's resistance to erosion-corrosion ensures reliable operation despite constant seawater exposure. These plates, manufactured to comply with stringent ASME, ASTM, and JIS standards, maintain their structural and corrosion-resistant properties even after years of service in marine conditions. The customization options available—with widths between 1000-3000mm—allow shipbuilders to optimize material usage for specific vessel designs. Additionally, the strong metallurgical bonding achieved through explosion welding ensures that these plates maintain their integrity despite the vibration and flexing common in maritime applications, making them ideal for long-term deployment in challenging ocean environments.
Manufacturing Processes for Superior Performance
The exceptional performance of Titanium Clad Steel Plates stems directly from sophisticated manufacturing techniques that create true metallurgical bonds between dissimilar metals. These processes ensure optimal material properties for demanding industrial applications.
Explosive Bonding Technology
Explosive bonding represents the pinnacle of cladding technology for creating Titanium Clad Steel Plates with unmatched bond integrity. This sophisticated process begins with meticulous surface preparation of both the titanium and steel components to remove contaminants and create optimal bonding conditions. Technicians at specialized facilities like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials arrange the materials in a precise configuration with carefully calculated standoff distances. The explosive material, distributed evenly across the surface, creates a controlled detonation wave that drives the titanium against the steel substrate at supersonic speeds. This high-velocity collision generates momentary extreme pressure and localized heating at the interface, creating a wavelike pattern bond where the materials actually intermix at the molecular level. The resulting composite plate demonstrates tensile bond strengths exceeding 70,000 psi—far surpassing the strength of adhesive bonding methods. What makes explosive bonding particularly valuable for Titanium Clad Steel Plates is its ability to join these dissimilar metals without significant heat input, thereby preserving the individual mechanical properties of both materials while creating an inseparable composite structure that resists delamination even under extreme stress conditions.
Roll Bonding Processes
Roll bonding delivers exceptional material uniformity for Titanium Clad Steel Plates designed for pressure vessel and heat transfer applications. This process begins with surface preparation where both the titanium and steel surfaces undergo degreasing, mechanical roughening, and chemical treatment to enhance bonding potential. The prepared materials are stacked with the titanium layer positioned precisely on the steel substrate before undergoing a controlled heating cycle that brings the assembly to approximately 60% of titanium's melting point. The heated package then passes through specially designed rolling mills where tremendous pressure—often exceeding 50,000 psi—forces the materials together while simultaneously reducing their combined thickness by 50-60%. This deformation breaks surface oxides and exposes fresh metal that forms atomic bonds across the interface. The rolled composite undergoes precision heat treatment to relieve residual stresses while enhancing the diffusion bonding process at the molecular level. This technique produces Titanium Clad Steel Plates with exceptionally uniform cladding thickness across large surface areas—critical for applications requiring predictable corrosion allowances and heat transfer properties. The resulting plates demonstrate superior flatness and dimensional stability, making them ideal for fabricating heat exchangers and pressure vessels where tight tolerances must be maintained.
Quality Control and Testing Protocols
The exceptional reliability of Titanium Clad Steel Plates stems from rigorous quality control systems implemented throughout the manufacturing process. Each plate undergoes ultrasonic testing using advanced phased array technology that identifies potential bonding defects as small as 6mm in diameter—far exceeding international standards requirements. Technicians perform shear strength testing on sample sections from each production batch, ensuring bond strengths consistently exceed 70 MPa as required by ASTM A264 specifications. The cladding ratio integrity undergoes verification through precision thickness measurements using laser profiling systems accurate to within 0.01mm. Additionally, Baoji JL implements comprehensive positive material identification (PMI) testing using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy to verify both the titanium cladding and steel substrate meet exact compositional requirements. Side bend testing evaluates the ductility of the bond interface by forcing samples to bend 180 degrees around mandrels without showing separation or cracking. For plates destined for critical service environments, accelerated corrosion testing in simulated process fluids verifies the titanium layer's protective capabilities under actual service conditions. This comprehensive testing regime, combined with ISO9001-2000 quality management systems and recently acquired PED and ABS international certifications in 2024, ensures that each Titanium Clad Steel Plate delivers consistent, reliable performance even in the most demanding industrial applications.

Application-Specific Benefits and Considerations
Understanding the unique advantages of Titanium Clad Steel Plates in specific industrial contexts helps engineers select the optimal material configuration for their applications. These benefits extend beyond basic corrosion resistance to include economic and operational advantages.
Corrosion Resistance in Aggressive Environments
Titanium Clad Steel Plates demonstrate exceptional performance in environments where conventional materials rapidly deteriorate. The titanium layer, typically Grade 1 or Grade 2 commercially pure titanium, creates an instantaneous passive oxide film that remains stable even when exposed to chloride-rich environments that would quickly destroy stainless steel components. This remarkable corrosion resistance derives from titanium's ability to maintain its protective oxide layer even in reducing acid conditions where stainless steels become vulnerable. In chemical processing applications involving hot hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, or chloride-containing process streams, Titanium Clad Steel Plates maintain their structural integrity for decades without significant metal loss. The customizable cladding thickness—ranging from 1.5mm to 5mm on plate thicknesses between 3mm and 200mm—allows engineers to specify the optimal corrosion allowance for specific service conditions. The explosion bonding technique creates a true metallurgical bond without heat-affected zones that might compromise corrosion resistance. Additionally, the material's resistance extends beyond simple uniform corrosion to include excellent protection against localized attack mechanisms like pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking that typically limit the service life of conventional alloys in challenging chemical environments.
Cost-Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Titanium Clad Steel Plates represent a strategic economic solution for industries requiring corrosion resistance without the prohibitive cost of solid titanium construction. The composite structure utilizes relatively thin titanium layers (typically 10-20% of total thickness) bonded to less expensive carbon or stainless steel, reducing material costs by 60-70% compared to solid titanium equivalents while maintaining comparable corrosion performance. This approach optimizes capital expenditure while ensuring equipment longevity in corrosive environments. The superior mechanical properties of the steel backing allow for thinner overall wall thicknesses compared to non-metallic alternatives like fiberglass or lined steel, resulting in more compact equipment designs and reduced installation footprints. Lifecycle cost analysis demonstrates that Titanium Clad Steel Plates, though initially more expensive than conventional stainless steels, deliver substantially lower total ownership costs through extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements. Fabricators appreciate that these composite plates can be formed, welded, and machined using conventional equipment with only moderate modifications to standard procedures. The delivery cycle of 3-6 months (negotiable) enables realistic project planning, while flexible transportation options including sea freight, air freight, and road transport facilitate global deployment. Equipment constructed from these plates typically achieves service lives exceeding 25 years even in the most challenging environments, making them the preferred choice for capital-intensive projects where reliability and longevity directly impact return on investment.
Fabrication Techniques and Design Considerations
Successful implementation of Titanium Clad Steel Plates requires specialized knowledge of fabrication techniques optimized for these composite materials. Welding procedures must address the dissimilar metal interface while preventing contamination of the titanium surface. Advanced fabricators employ automated GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) systems with trailing shield gas coverage to maintain titanium's metallurgical integrity during fusion welding operations. Cold forming operations—such as rolling, pressing, and bending—require careful control of bend radii and deformation rates to prevent stress concentration at the clad interface. Designers must incorporate transition joints at nozzle connections where titanium-clad surfaces interface with other metallic components, typically using explosion-bonded transition pieces that provide reliable dissimilar metal junctions. Heat exchanger designs benefit from the superior thermal conductivity of these composite plates while avoiding galvanic coupling issues through strategic isolation of dissimilar metal contacts. Engineering teams must consider differential thermal expansion characteristics when designing equipment that experiences significant temperature fluctuations, incorporating flexibility elements that accommodate the different expansion rates of titanium and steel. The surface treatment options—including polishing, sandblasting, and acid pickling—enable optimization for specific process environments, with polished surfaces providing superior resistance to product adhesion and fouling in viscous fluid applications. This technical expertise, combined with Baoji JL's ability to provide plates in customized dimensions up to 3,000mm width and 12,000mm length, enables the construction of sophisticated chemical processing equipment that maximizes performance while minimizing total installed cost.
Conclusion
Titanium Clad Steel Plates have established themselves as indispensable materials across multiple industries facing corrosive environments and demanding mechanical requirements. Their unique combination of titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance with steel's structural strength creates an economically viable solution for equipment with extended service life requirements in challenging conditions.
Are you facing challenging material selection decisions for your next industrial project? Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials offers innovative solutions through our advanced Titanium Clad Steel Plates. With our independent explosive composite technology, international certifications including ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS (achieved in 2024), and extensive R&D capabilities, we deliver customized solutions for your specific application needs. Our ODM/OEM services ensure you receive exactly what your project requires. Contact our engineering team today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our technological superiority can provide innovative, long-lasting solutions for your most demanding applications.
References
1. Johnson, R.T. & Wilson, K.L. (2023). "Advanced Materials for Chemical Processing Equipment: A Comprehensive Review of Clad Metals." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 32(4), 1823-1839.
2. Chen, W., Zhang, H., & Thompson, S. (2022). "Corrosion Resistance of Titanium-Steel Composites in Marine Environments." Corrosion Science, 175, 108862.
3. Patel, V.R. & Sharma, A.K. (2023). "Economic Assessment of Clad Materials versus Solid Alloys in Pressure Vessel Design." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 198, 104684.
4. Williams, J.C. & Luthra, K.L. (2021). "Explosive Welding Techniques for Dissimilar Metals in Industrial Applications." Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 64, 1236-1251.
5. Nakamura, T., Tanaka, Y., & Smith, P.D. (2022). "Quality Control Standards for Titanium Clad Steel in Critical Service Applications." Materials Evaluation, 80(5), 527-543.
6. Harrison, B.L. & Martin, S.J. (2024). "Long-term Performance of Titanium Clad Equipment in Oil Refining Operations: A 20-Year Case Study." Materials Performance, 63(2), 55-63.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)