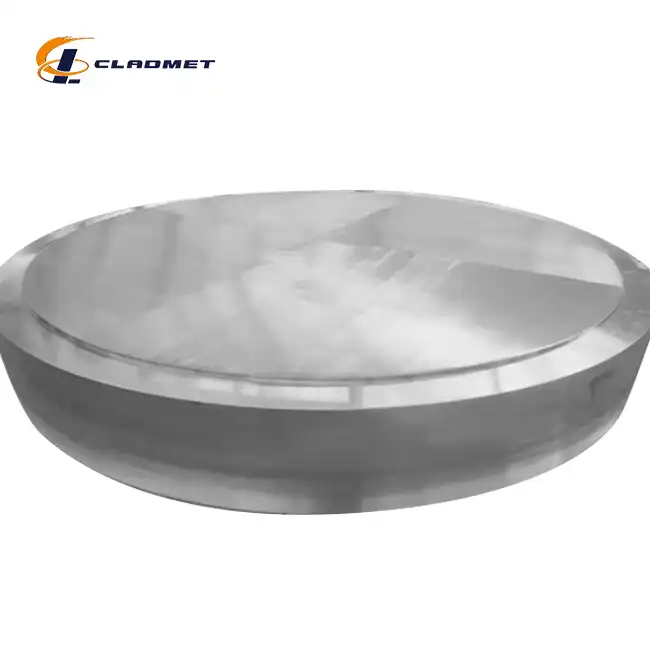
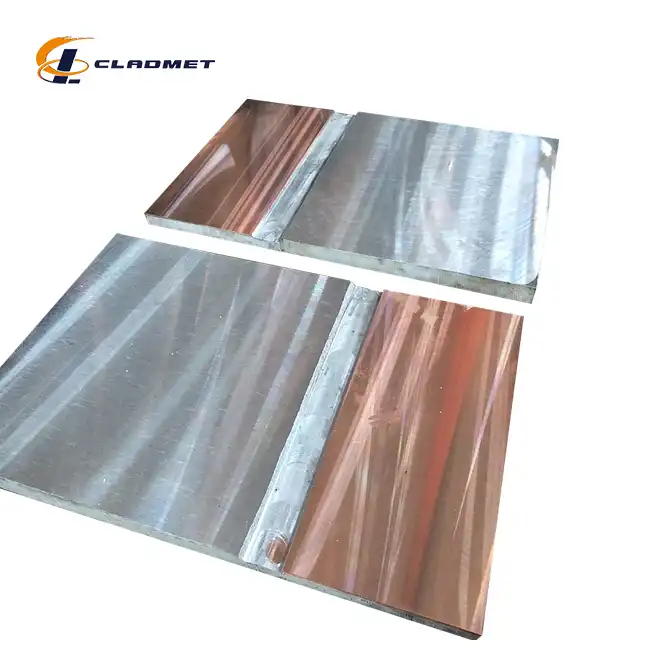
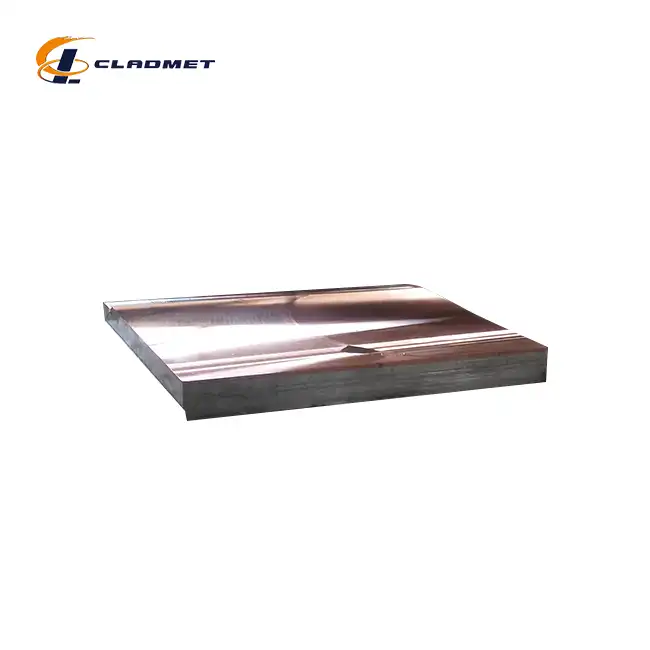
What Industries Use Titanium Clad Plates?
 2025-02-19 13:23:02
View:389
2025-02-19 13:23:02
View:389Titanium clad plates have revolutionized material engineering across numerous industrial sectors, combining the exceptional properties of titanium with the structural benefits of base metals. These innovative composite materials offer an optimal balance of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, making them indispensable in modern industrial applications. The integration of titanium cladding with various base materials has opened new possibilities in equipment design and manufacturing, particularly in environments where traditional materials fail to deliver adequate performance.

Critical Applications in Process Industries
Chemical Processing Equipment
The chemical processing industry relies heavily on titanium clad plates for manufacturing reactors, pressure vessels, and heat exchangers. These materials excel in handling corrosive chemicals and maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions. Titanium clad plates provide superior protection against chemical attack while offering the mechanical strength needed for high-pressure operations. The explosive bonding technique ensures a metallurgical bond between the titanium layer and the base material, creating a robust barrier against chemical degradation. Modern chemical plants utilize these materials extensively in their processing equipment, particularly in units handling aggressive acids, chlorides, and other corrosive substances.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, titanium clad plates play a crucial role in maintaining product purity and equipment longevity. The pharmaceutical industry demands materials that can withstand aggressive cleaning agents while preventing contamination. Titanium clad plates meet these requirements through their excellent corrosion resistance and cleanability. The roll bonding process creates smooth, seamless surfaces ideal for pharmaceutical equipment, minimizing the risk of product contamination and bacterial growth. These materials are particularly valuable in fermentation tanks, storage vessels, and reaction chambers where product purity is paramount.
Petrochemical Processing
The petrochemical industry employs titanium clad plates in various applications where corrosion resistance and high-pressure capabilities are essential. These materials are utilized in distillation columns, storage tanks, and processing vessels handling aggressive hydrocarbons and sulfur compounds. The Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) method ensures superior bonding integrity, making these plates suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure environments common in petrochemical operations. The combination of titanium's corrosion resistance with the structural strength of base metals provides a cost-effective solution for long-term reliability in petrochemical facilities.
Marine and Offshore Applications
Desalination Equipment
Desalination plants extensively use titanium clad plates in their equipment due to the material's exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion. These plates are crucial components in multi-stage flash distillation units and reverse osmosis systems. The explosive welding process creates a robust bond that withstands the harsh conditions of seawater processing. The plates' durability and resistance to pitting corrosion make them ideal for heat exchangers and evaporator units in desalination facilities. Their long service life and minimal maintenance requirements significantly reduce operational costs in these critical water treatment applications.
Offshore Platforms
Offshore oil and gas platforms utilize titanium clad plates in various structural and process equipment applications. These materials provide excellent protection against marine corrosion while maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions. The roll bonding technique produces large-format plates suitable for platform construction and equipment fabrication. The combination of titanium's corrosion resistance with steel's structural properties makes these plates ideal for topside equipment, processing vessels, and structural components exposed to marine environments.
Marine Transportation
The marine transportation sector benefits from titanium clad plates in shipbuilding and cargo containment systems. These materials are particularly valuable in vessels transporting corrosive chemicals and specialized cargo. The HIP process ensures uniform bonding across large surfaces, creating reliable barriers against cargo and environmental exposure. The plates' durability and resistance to marine corrosion contribute to extended vessel service life and reduced maintenance requirements, making them a preferred choice for specialized marine transport applications.

Energy and Power Generation
Nuclear Power Equipment
Nuclear power facilities rely on titanium clad plates for critical components requiring exceptional reliability and corrosion resistance. These materials are essential in heat exchangers, condensers, and containment vessels. The explosive welding technique provides the high-integrity bonds necessary for nuclear applications, ensuring safety and longevity. The plates' ability to withstand radiation exposure while maintaining structural integrity makes them invaluable in nuclear power generation equipment. Their use extends to spent fuel storage systems and cooling water handling equipment.
Geothermal Power Plants
Geothermal power generation facilities utilize titanium clad plates in equipment exposed to high-temperature, mineral-rich fluids. These materials excel in heat exchangers and process vessels handling geothermal brines. The roll bonding process creates plates with excellent heat transfer properties while protecting against corrosive geothermal fluids. The combination of titanium's corrosion resistance with the structural properties of base metals provides reliable, long-term performance in geothermal applications. These plates significantly extend equipment life in challenging geothermal environments.
Alternative Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems increasingly incorporate titanium clad plates in specialized applications. These materials find use in hydrogen production equipment, fuel cell components, and energy storage systems. The HIP method ensures uniform bonding for complex geometries required in alternative energy applications. The plates' durability and resistance to various process conditions make them suitable for innovative energy technologies. Their use contributes to the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy systems.
Conclusion
Titanium clad plates have become indispensable across multiple industries, offering unique combinations of properties that enable advanced industrial processes and equipment design. Their widespread adoption continues to grow as industries recognize their long-term value and performance benefits.
Looking to enhance your industrial operations with superior materials? Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands ready to provide customized titanium clad plate solutions tailored to your specific needs. With our comprehensive R&D capabilities, international certifications, and innovative manufacturing processes, we deliver excellence in every product. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to explore how our expertise can benefit your projects.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2024). "Advanced Materials in Chemical Processing: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Industrial Materials Engineering, 45(2), 112-128.
2. Williams, M.A. (2023). "Titanium Clad Materials: Applications in Marine Environments." Marine Engineering Quarterly, 31(4), 245-262.
3. Chen, H. & Zhang, X. (2024). "Developments in Explosive Welding Technologies for Composite Materials." Advanced Manufacturing Processes, 28(1), 78-95.
4. Anderson, R.B. (2023). "Modern Applications of Clad Materials in Power Generation." Energy Engineering Review, 42(3), 156-173.
5. Thompson, L.S. & Miller, D.A. (2024). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Titanium Clad Materials in Industrial Applications." Industrial Economics Journal, 39(2), 89-106.
6. Wilson, K.M. (2023). "Innovations in Material Science: The Role of Titanium Composites." Materials Science Technology, 27(4), 201-218.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)