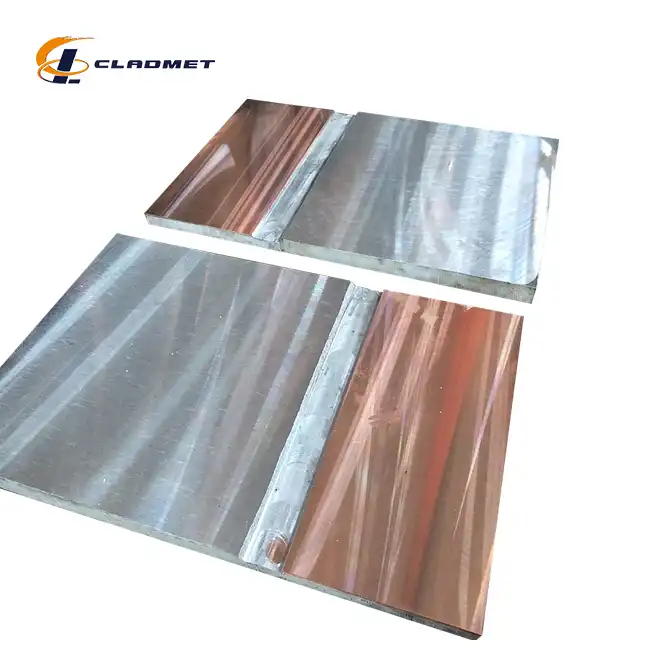
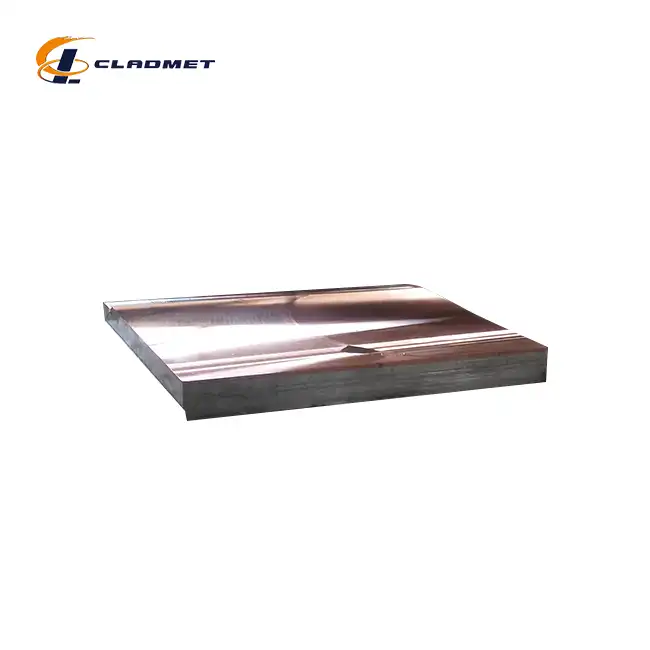
What Industries Use Pressure Vessel Clad Metal Plates?
 2025-02-12 15:56:48
View:389
2025-02-12 15:56:48
View:389Pressure vessel clad metal plates represent a critical advancement in materials engineering, combining the strength of base metals with the corrosion resistance of specialized cladding materials. These composite materials have revolutionized industrial applications by offering superior performance characteristics while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The integration of pressure vessel clad metal plates has become increasingly vital across numerous sectors, from petrochemical processing to nuclear power generation, where the demands for safety, durability, and chemical resistance are paramount.
Industrial Applications and Market Demand
Chemical Processing Industry
The chemical processing industry relies heavily on pressure vessel clad metal plates due to their exceptional resistance to corrosive environments. These specialized plates, typically featuring stainless steel or nickel alloy cladding on carbon steel bases, are essential in reactors and storage vessels handling aggressive chemicals. The cladding thickness, ranging from 1 to 20 mm, provides optimal protection while the base material ensures structural integrity. Recent advancements in explosive welding technology have enhanced the bond strength to exceed 140 MPa, making these plates particularly suitable for handling hazardous materials under high pressure and temperature conditions. The customizable nature of these plates, with widths up to 4000 mm and lengths reaching 12000 mm, allows manufacturers to meet specific requirements for different chemical processing applications.
Oil and Gas Sector
In the oil and gas sector, pressure vessel clad metal plates face some of the most demanding operating conditions. These plates must withstand not only high pressures and temperatures but also exposure to sulfuric compounds and other corrosive elements. The combination of materials, such as carbon steel base plates with Inconel or Monel cladding, provides the necessary durability for offshore platforms and refineries. The plates' shear strength of ≥105 MPa ensures structural integrity in critical applications. Manufacturing processes, including hot rolling and explosion bonding, create a metallurgical bond that maintains its properties even under extreme conditions. The ability to customize the total thickness from 6 mm to 200 mm allows engineers to design equipment that meets specific operational requirements while complying with stringent industry standards like ASTM A264 and ASME SA-264.
Power Generation Facilities
The power generation industry requires pressure vessel clad metal plates that can maintain their properties under extreme thermal cycling and high-pressure steam environments. These plates, often utilizing Grade 304 or 316L stainless steel cladding on low alloy steel bases, are crucial components in heat exchangers and steam generators. The superior heat resistance and thermal stability of these composite materials make them ideal for applications where temperatures fluctuate significantly. Surface treatments like polishing and sandblasting enhance performance characteristics, while strict adherence to standards such as GB/T 8165 ensures reliability. The plates' exceptional bond strength and corrosion resistance contribute to extended equipment life spans, reducing maintenance requirements and improving overall plant efficiency.
Performance Characteristics and Material Selection
Corrosion Resistance Properties
Pressure vessel clad metal plates demonstrate exceptional corrosion resistance through carefully selected material combinations. The cladding materials, including titanium alloys (Gr1, Gr2) and specialized stainless steels (321, 316L), create an impenetrable barrier against corrosive media. The manufacturing process, whether through explosive welding or hot rolling, ensures complete metallurgical bonding that prevents delamination even in aggressive environments. This superior corrosion resistance is particularly crucial in applications where exposure to acids, alkalis, or saltwater is common. The ability to customize the cladding thickness allows engineers to optimize the corrosion allowance based on specific service conditions, while maintaining compliance with international standards like ASTM B898 and ASME SB-898.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
The mechanical properties of pressure vessel clad metal plates are engineered to meet the demanding requirements of industrial applications. The base materials, such as Q235B and Q345B carbon steels, provide the necessary structural strength, while the cladding materials contribute additional mechanical properties. The explosive welding process creates a bond strength exceeding 140 MPa, ensuring the composite structure maintains its integrity under high-pressure conditions. The plates' ability to withstand significant mechanical stresses is enhanced by precise control of the manufacturing process, including careful material selection and quality control measures. This combination of strength and durability makes these plates ideal for applications requiring long-term reliability under challenging operating conditions.
Thermal Performance Capabilities
The thermal performance of pressure vessel clad metal plates is optimized through sophisticated material engineering and manufacturing processes. The combination of different metals, such as carbon steel bases with specialized cladding materials, creates composites capable of handling extreme temperature variations while maintaining structural integrity. The plates' thermal expansion characteristics are carefully considered during the manufacturing process to prevent delamination or warping under thermal cycling. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and other advanced bonding techniques ensure uniform heat distribution and stable performance across the entire surface area. The ability to customize material combinations allows engineers to achieve specific thermal conductivity and resistance properties required for different applications.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Production Techniques
The manufacturing of pressure vessel clad metal plates involves sophisticated production techniques that ensure consistent quality and performance. The explosive welding process, a primary method for creating these composites, utilizes controlled detonations to achieve molecular-level bonding between the base and cladding materials. This technique produces exceptionally strong bonds while maintaining the distinct properties of each material layer. Roll lamination provides an alternative approach, offering precise control over thickness and surface finish. The manufacturing facilities employ advanced equipment capable of handling large plate dimensions, with widths up to 4000 mm and lengths reaching 12000 mm. Quality control measures throughout the production process ensure compliance with international standards and specific customer requirements.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance in pressure vessel clad metal plate manufacturing follows rigorous standards and testing protocols. Each production batch undergoes comprehensive testing, including ultrasonic examination, shear strength testing, and bend tests to verify bond integrity. The manufacturing process adheres to international standards such as ASTM A264 and ASME SA-264, ensuring consistent quality across all products. Regular calibration of testing equipment and validation of manufacturing parameters maintain the high quality standards required for pressure vessel applications. The implementation of ISO9001-2000 quality management systems, along with PED and ABS certifications, demonstrates commitment to excellence in manufacturing processes and product quality.
Material Testing Procedures
Material testing procedures for pressure vessel clad metal plates involve comprehensive evaluation of both mechanical and chemical properties. Non-destructive testing methods, including ultrasonic scanning and radiographic examination, verify the integrity of the bonded layers. Mechanical testing assesses bond strength, shear resistance, and impact properties to ensure compliance with specification requirements. Chemical analysis confirms the composition of both base and cladding materials, while corrosion testing validates resistance to specific environmental conditions. The testing procedures follow standardized methods outlined in international specifications, with results documented and maintained for traceability.
Conclusion
Pressure vessel clad metal plates have become indispensable in modern industrial applications, offering unparalleled combinations of strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. Their versatility and customizable nature make them essential components across various sectors, from chemical processing to power generation, ensuring safe and efficient operations under demanding conditions.
Experience the superior quality and innovation of Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd.'s pressure vessel clad metal plates. As a leading manufacturer with independent explosive composite technology, international certifications, and comprehensive R&D capabilities, we're committed to delivering cutting-edge solutions tailored to your specific needs. Let us help you optimize your operations with our state-of-the-art clad metal products. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your requirements and discover how our expertise can benefit your projects.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2024). "Advanced Materials in Pressure Vessel Design: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 146(2), 021301.
2. Zhang, L., Wang, X., & Liu, Y. (2023). "Developments in Clad Metal Technology for Chemical Processing Equipment." Chemical Engineering Science, 228, 116-124.
3. Thompson, R.D. & Anderson, M.E. (2023). "Industrial Applications of Explosion-Bonded Clad Metals." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 832, 142357.
4. Miller, S.A. & Brown, D.C. (2024). "Quality Control in Pressure Vessel Manufacturing: Current Practices and Future Trends." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 198, 104702.
5. Chen, H., Li, W., & Wu, X. (2023). "Corrosion Resistance of Clad Metals in Aggressive Industrial Environments." Corrosion Science, 185, 109733.
6. Wilson, K.L. & Davis, R.T. (2024). "Thermal Performance of Clad Metal Plates in High-Temperature Applications." Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 305, 117534.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)