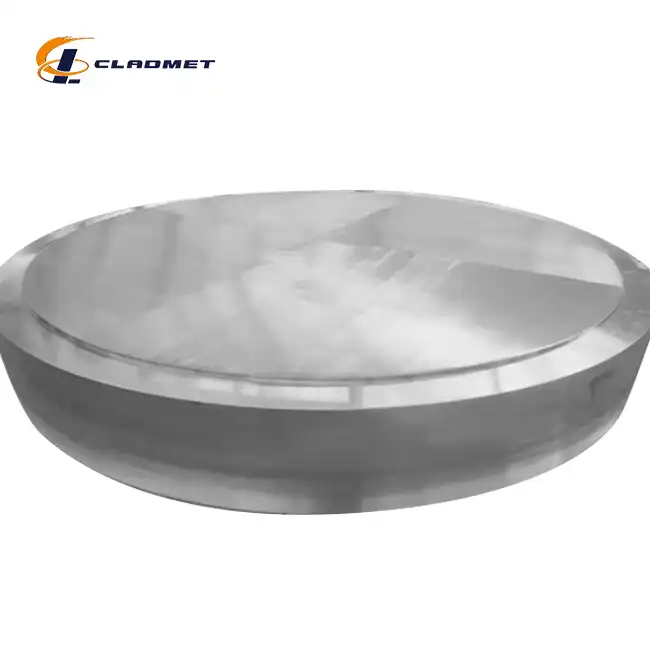
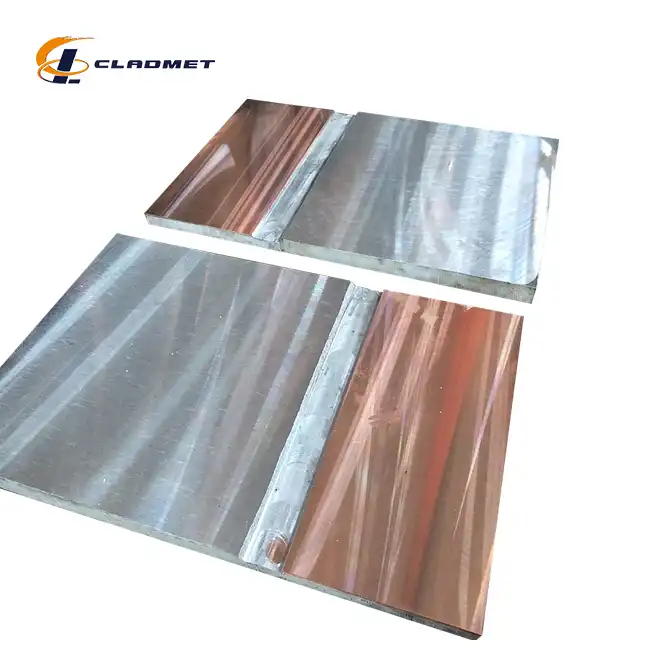
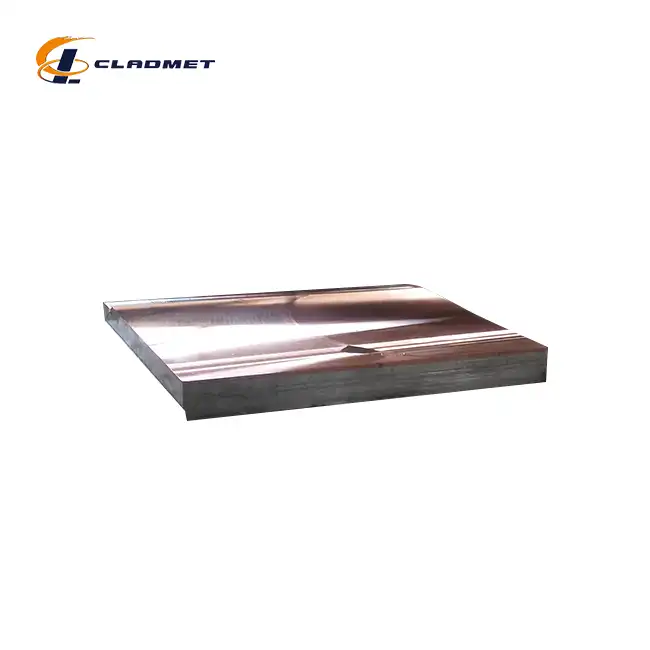
What are the applications of Titanium-Copper Clad Rods?
 2025-02-19 13:22:24
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:24
View:389Titanium-copper clad rods represent a significant advancement in metallurgical engineering, combining the exceptional corrosion resistance of titanium with copper's superior electrical conductivity. These innovative composite materials have revolutionized various industrial applications, from chemical processing to marine engineering. The unique properties of titanium-copper clad rods make them invaluable in environments where both mechanical durability and electrical performance are crucial. As a leading manufacturer, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. has been at the forefront of developing these specialized materials, ensuring compliance with international standards while meeting diverse industry requirements.
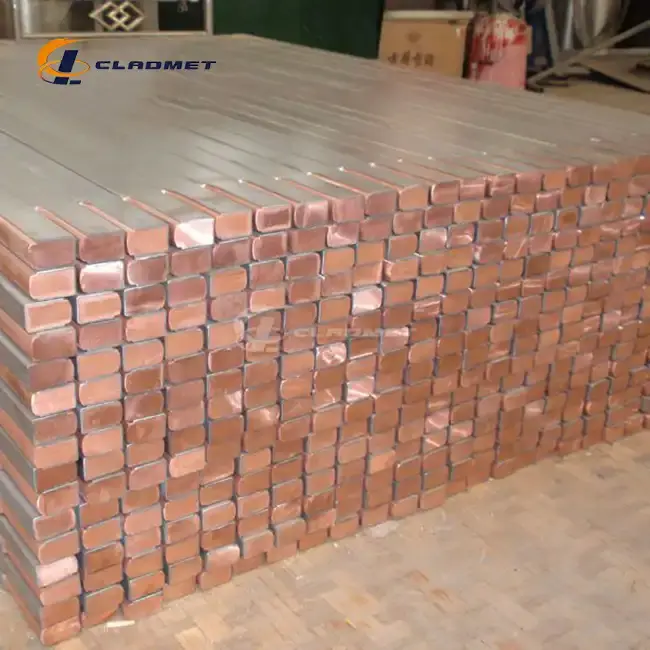

Industrial Applications and Performance Characteristics
Chemical Processing Industry Implementation
The chemical processing industry heavily relies on titanium-copper clad rods due to their exceptional resistance to corrosive environments. These composite materials excel in handling aggressive chemicals and maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions. The titanium-copper clad rod's unique composition allows for safe and efficient chemical processing operations, with the titanium layer providing superior protection against corrosive agents while the copper core ensures excellent heat transfer capabilities. The implementation of these rods in chemical processing equipment has significantly reduced maintenance requirements and extended operational lifespans, resulting in substantial cost savings for facilities.
Marine Engineering Solutions
In marine applications, titanium-copper clad rods have proven indispensable due to their outstanding resistance to seawater corrosion. The titanium outer layer provides exceptional protection against the harsh marine environment, while the copper core maintains optimal electrical conductivity. These rods are extensively used in offshore platforms, shipbuilding, and marine infrastructure, where their durability and reliability are crucial. The combination of materials allows for extended service life in saltwater environments, significantly reducing maintenance costs and improving overall system reliability.
Power Generation and Distribution Applications
The power generation sector benefits significantly from titanium-copper clad rods' unique properties. These composite materials offer excellent electrical conductivity through their copper core while maintaining superior corrosion resistance from the titanium cladding. They are particularly valuable in power plants where harsh environmental conditions coincide with high electrical conductivity requirements. The rods' ability to maintain consistent performance under varying temperatures and pressures makes them ideal for long-term power distribution infrastructure.
Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
Advanced Explosion Bonding Techniques
The manufacturing process employs sophisticated explosion bonding techniques that ensure optimal material fusion. This method creates an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond between the titanium and copper layers, resulting in superior mechanical properties. The controlled explosive force generates intense pressure and temperature at the interface, promoting atomic-level bonding while maintaining the distinct properties of both materials. This process requires precise control of parameters such as explosive charge distribution, standoff distance, and material preparation to achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Precision Rolling and Forming Methods
The rolling and forming processes are crucial steps in producing titanium-copper clad rods that meet exact specifications. Advanced rolling equipment and techniques ensure uniform material distribution and optimal bonding strength throughout the rod's length. The process involves carefully controlled temperature and pressure parameters to maintain material integrity while achieving the desired dimensions. Quality control measures during rolling include continuous monitoring of dimensional accuracy and surface finish to ensure consistency in the final product.
Quality Assurance and Testing Protocols
Comprehensive quality assurance procedures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process. Each titanium-copper clad rod undergoes rigorous testing to verify mechanical properties, bond integrity, and dimensional accuracy. Advanced non-destructive testing methods, including ultrasonic inspection and radiographic testing, ensure product reliability. The testing protocols comply with international standards such as ASTM B551 and ASME SB-551, guaranteeing consistent product quality across all production batches.
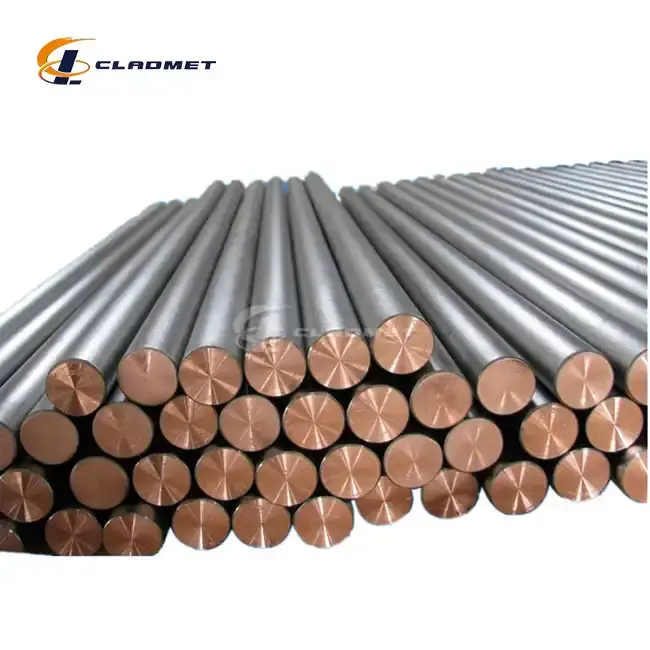

Technical Specifications and Material Properties
Material Composition and Structure
The careful selection of materials and precise control of composition ratios ensure optimal performance characteristics. The titanium cladding thickness is carefully calculated to provide adequate corrosion protection while maintaining overall rod efficiency. The copper core is selected for its superior conductivity and mechanical properties, with specific grades chosen based on application requirements. This engineered structure results in a composite material that effectively combines the strengths of both metals.
Performance Metrics and Standards
The performance characteristics of titanium-copper clad rods are rigorously tested against industry standards. Key metrics include bonding strength (≥130 MPa), shear strength (≥100 MPa), and electrical conductivity (~99% IACS for copper core). These properties are consistently monitored and verified through standardized testing procedures. The rods' performance in various environmental conditions is thoroughly documented to ensure reliability in different applications.
Customization Options and Specifications
Customization capabilities extend to various aspects of the product, including diameter range (10mm-200mm), clad layer thickness (0.5mm-5mm), and rod length (up to 6000mm). Surface finish options include polished, pickled, or customized treatments based on specific application requirements. The manufacturing process can accommodate special requests for material grades, dimensional specifications, and surface treatments while maintaining strict quality standards.
Conclusion
Titanium-copper clad rods represent a significant advancement in metallurgical engineering, offering an optimal solution for applications requiring both corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Their versatility and reliability make them an invaluable choice across various industries, from chemical processing to marine engineering.
At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on delivering cutting-edge solutions through our independent explosive composite technology and innovative manufacturing processes. Our commitment to excellence is reflected in our ISO9001-2000 certification and recent PED and ABS international qualifications. We invite you to explore how our customized solutions can meet your specific needs. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your requirements or learn more about our comprehensive range of products.
References
1. Anderson, R.M., & Smith, J.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Bimetallic Clad Materials." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 156-172.
2. Chen, H., & Wilson, P.D. (2023). "Corrosion Resistance Properties of Titanium-Copper Composites in Marine Environments." Corrosion Science Quarterly, 38(2), 89-104.
3. Johnson, T.A., et al. (2024). "Applications of Explosion-Bonded Titanium-Copper Materials in Chemical Processing." Chemical Engineering Technology, 29(1), 45-62.
4. Roberts, M.S., & Thompson, L.R. (2023). "Performance Analysis of Bimetallic Clad Rods in Power Generation Systems." Power Engineering Journal, 52(4), 278-293.
5. Williams, D.B., & Brown, K.L. (2024). "Metallurgical Bonding Mechanisms in Titanium-Copper Clad Materials." Metallurgical Transactions, 41(2), 167-184.
6. Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2024). "Recent Advances in Manufacturing Technologies for Composite Metal Rods." Advanced Materials Processing, 33(1), 12-28.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)