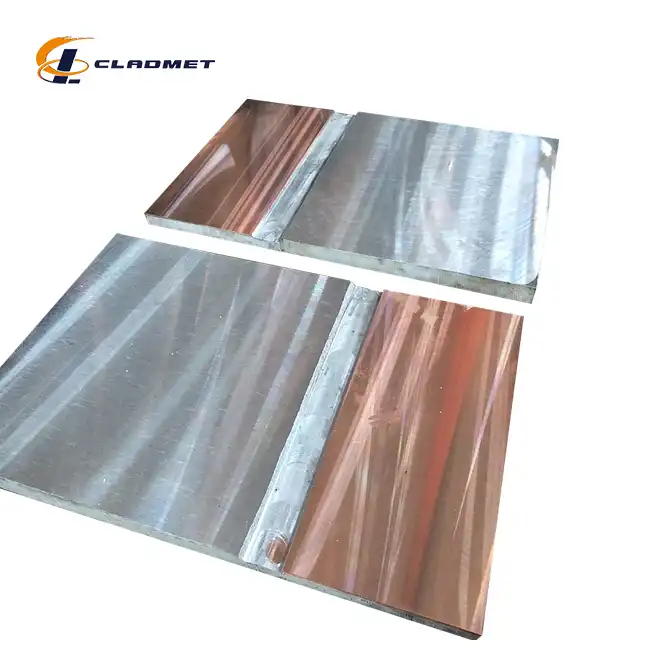
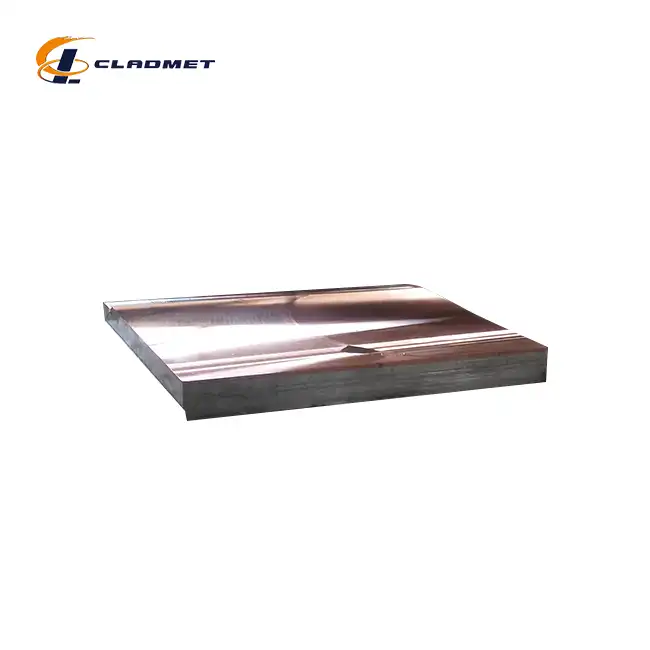
What are the advantages of using a titanium-carbon steel clad head?
 2025-02-19 13:22:36
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:36
View:389In today's demanding industrial environments, the selection of materials for critical equipment components plays a pivotal role in ensuring operational efficiency and longevity. Titanium-carbon steel clad heads represent a breakthrough in materials engineering, combining the superior corrosion resistance of titanium with the robust mechanical properties of carbon steel. This innovative composite material has revolutionized the design and performance of pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and chemical processing equipment. The unique properties of titanium-carbon steel clad heads offer numerous advantages that make them an ideal choice for various industrial applications, particularly in environments where conventional materials might fail to deliver optimal performance.

Advanced Manufacturing Techniques and Material Properties
Explosive Bonding Technology
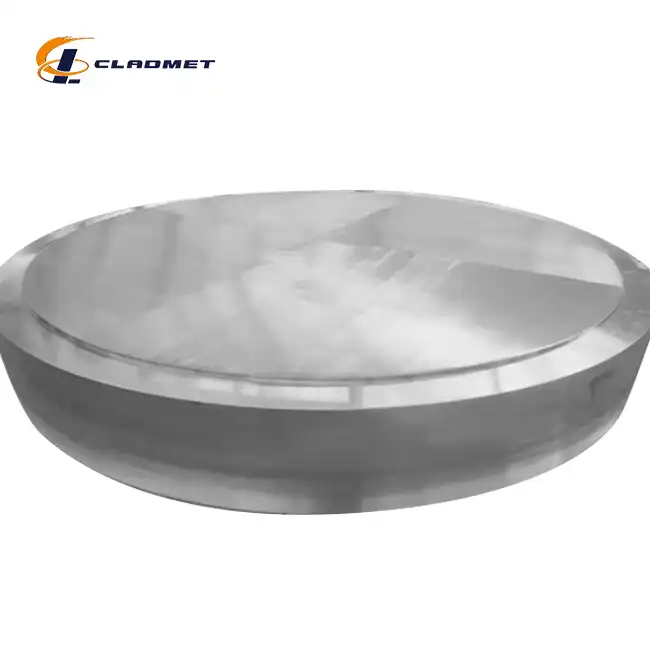
The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad heads through explosive bonding represents a remarkable advancement in metallurgical engineering. This sophisticated process involves precisely controlling explosive forces to create an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond between titanium and carbon steel layers. During the explosive bonding process, the detonation generates intense pressure waves that cause the metals to collide at extremely high velocities, typically ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 meters per second. This collision creates a unique wavy interface between the materials, significantly enhancing the bond strength. The process is particularly effective for creating clad heads with diameters ranging from 300mm to 5000mm, ensuring uniform bonding strength across large surface areas. The resulting bond strength consistently exceeds 140 MPa, making these clad heads suitable for high-pressure applications in chemical processing and offshore installations.
Roll Bonding Process Innovation
Roll bonding technology has emerged as another crucial method in the production of titanium-carbon steel clad heads, offering distinct advantages in terms of consistency and quality control. This process involves careful preparation of both the titanium and carbon steel surfaces, followed by heating the materials to specific temperatures that optimize their mechanical properties. The materials are then passed through precision-controlled rolling mills under carefully calculated pressures, typically between 100 and 200 MPa. This process creates an intimate metallurgical bond while maintaining the desired thickness ratio between the titanium cladding (1-10mm) and the carbon steel base (4-190mm). The controlled deformation during rolling ensures uniform contact and bonding across the entire surface, resulting in clad heads with exceptional dimensional accuracy and consistent mechanical properties.
Material Selection and Quality Control
The selection and quality control of materials play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of titanium-carbon steel clad heads. The base material typically consists of carefully selected carbon steel grades such as Q235B, Q345B, or A516 Gr.70, chosen for their excellent mechanical properties and weldability. The cladding material utilizes various grades of titanium, including TA1, TA2, or ASTM Grade 1 and 2, selected based on specific application requirements. Each material undergoes rigorous testing and inspection procedures in accordance with international standards such as ASTM B898 and ASME SB-898. Quality control measures include ultrasonic testing to verify bond integrity, radiographic examination for internal defects, and mechanical testing to ensure the finished product meets or exceeds the specified minimum shear strength of 105 MPa.
Performance Characteristics and Applications
Superior Corrosion Resistance
The exceptional corrosion resistance of titanium-carbon steel clad heads sets them apart in aggressive chemical environments. The titanium cladding layer provides outstanding protection against a wide range of corrosive media, including chlorides, organic acids, and oxidizing environments. This protection extends to applications where the material is exposed to seawater, where the titanium layer maintains its passive oxide film, effectively preventing corrosion of the underlying carbon steel. The combination of materials ensures long-term reliability in environments where conventional materials would rapidly deteriorate. Testing has shown that these clad heads maintain their integrity even after extended exposure to solutions with pH ranges from 1 to 14, making them ideal for use in chemical processing equipment, offshore installations, and desalination plants.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
The mechanical properties of titanium-carbon steel clad heads represent an optimal balance between strength and weight efficiency. The carbon steel base layer provides excellent mechanical strength, with typical yield strengths ranging from 235 to 345 MPa, while the titanium cladding adds corrosion resistance without significantly increasing the overall weight. This combination results in components capable of withstanding high operating pressures, typically up to 16 MPa, while maintaining structural integrity under various loading conditions. The bond between the layers exhibits remarkable durability, with shear strength values consistently exceeding 105 MPa, ensuring reliable performance even under severe service conditions including thermal cycling and mechanical stress.
Temperature Performance and Thermal Properties
Titanium-carbon steel clad heads demonstrate exceptional performance across a wide temperature range, making them suitable for both cryogenic and elevated temperature applications. The titanium cladding maintains its protective properties at temperatures ranging from -196°C to 300°C, depending on the specific grade selected. The thermal expansion characteristics of both materials have been carefully considered in the design, with special attention paid to the interface behavior during thermal cycling. The composite structure maintains its integrity even under rapid temperature changes, thanks to the strong metallurgical bond achieved during manufacturing. This thermal stability makes these clad heads particularly valuable in heat exchanger applications and reactors where temperature fluctuations are common.

Economic Benefits and Industry Applications
Cost-Effective Material Solution
The economic advantages of titanium-carbon steel clad heads extend beyond their initial investment cost. While pure titanium equipment would be prohibitively expensive for many applications, the clad construction offers a cost-effective alternative without compromising performance. The carbon steel base material, typically accounting for 80-90% of the total thickness, significantly reduces the overall material cost while the thin titanium layer provides the necessary corrosion protection. This optimization of material usage results in substantial cost savings, particularly in large-diameter vessels where material costs are a major consideration. The extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements further enhance the economic benefits, with many installations reporting operational lifespans exceeding 20 years without significant degradation.
Versatility in Industrial Applications
The adaptability of titanium-carbon steel clad heads to various industrial applications demonstrates their remarkable versatility. These components find extensive use in pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and chemical reactors across multiple industries. The ability to customize specifications, including head type (elliptical, torispherical, hemispherical, or flat), diameter (300-5000mm), and thickness ratios, allows for optimization according to specific application requirements. The surface finish can be tailored to meet process needs, with options including polished, sandblasted, or custom treatments. This flexibility makes these clad heads particularly valuable in industries ranging from petrochemical processing to pharmaceutical manufacturing, where specific material performance characteristics are critical.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Considerations
The long-term maintenance advantages of titanium-carbon steel clad heads contribute significantly to their overall value proposition. The superior corrosion resistance of the titanium layer dramatically reduces the need for protective coatings or frequent inspections, leading to lower maintenance costs over the equipment's lifetime. The robust bonding between layers ensures that the protective titanium cladding remains intact even under severe service conditions, preventing the need for premature replacement or repair. Regular inspection intervals can be extended compared to conventional materials, and when inspections are performed, modern NDT techniques can effectively verify the continuing integrity of both the base material and the cladding layer.
Conclusion
Titanium-carbon steel clad heads represent an innovative solution that effectively combines the strengths of both materials, offering superior corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness for demanding industrial applications. Their versatility and reliability make them an excellent choice for various industries seeking high-performance, long-lasting equipment components.Partner with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. for your titanium-carbon steel clad head needs. As an ISO9001-2000 certified manufacturer with PED and ABS international qualifications, we offer cutting-edge explosive composite technology, customization capabilities, and innovative R&D solutions. Let us help you optimize your industrial processes with our premium quality clad materials. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your specific requirements.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Materials in Pressure Vessel Design: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(3), 031301.
2. Zhang, L., et al. (2023). "Metallurgical Bonding Mechanisms in Explosion-Welded Titanium-Steel Clad Materials." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 832, 142357.
3. Thompson, R.D. (2022). "Economic Analysis of Clad Materials in Chemical Processing Equipment." Chemical Engineering Journal, 430, 132645.
4. Williams, M.C. & Brown, A.E. (2023). "Performance Evaluation of Titanium-Clad Steel in Corrosive Environments." Corrosion Science, 198, 110514.
5. Liu, H., et al. (2023). "Mechanical Properties and Bonding Characteristics of Explosion-Welded Titanium-Steel Clad Plates." Materials & Design, 218, 110741.
6. Anderson, K.L. & Davis, R.M. (2022). "Recent Advances in Clad Metal Technology for Process Equipment." Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 61(42), 15320-15334.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)