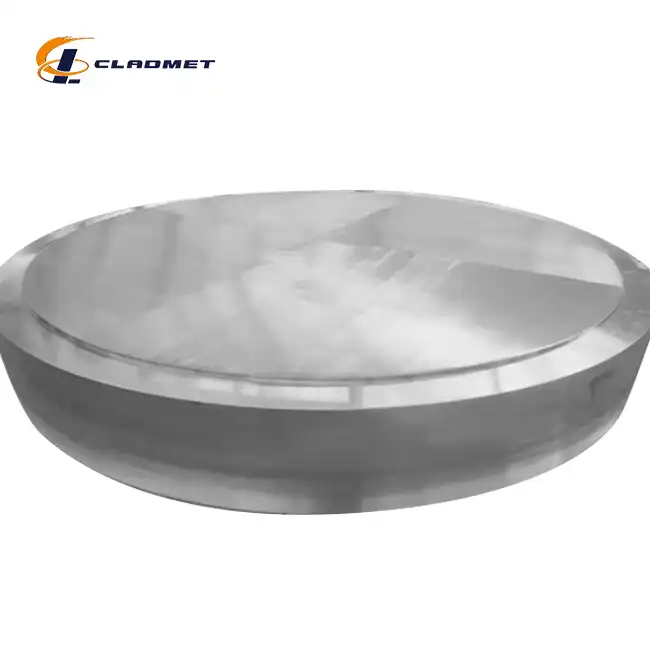
How is Titanium-Carbon Steel Cladding Applied?
 2025-02-19 13:22:34
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:34
View:389The application of titanium-carbon steel cladding represents a significant advancement in materials engineering, combining the superior corrosion resistance of titanium with the structural strength and cost-effectiveness of carbon steel. This innovative cladding process creates a highly durable composite material that finds extensive use in demanding industrial applications. The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad heads involves sophisticated bonding technologies that ensure optimal performance across various operational conditions while maintaining structural integrity and chemical resistance.
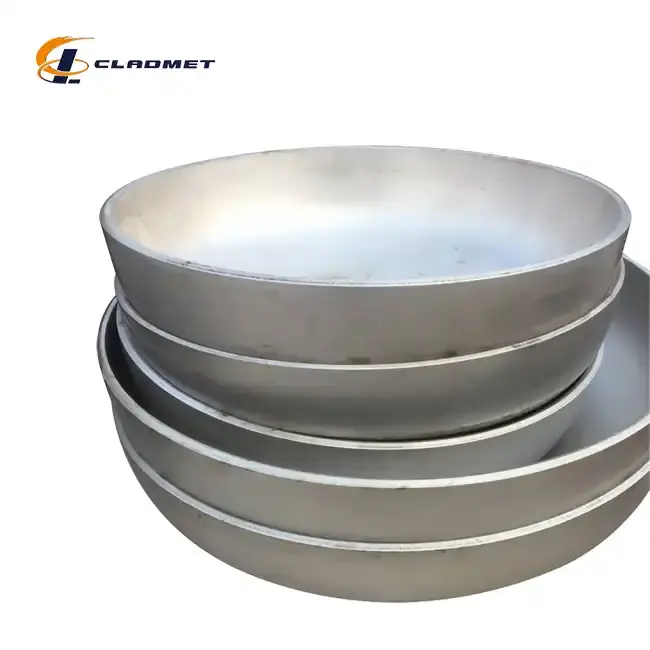

Manufacturing Processes and Technical Specifications
Advanced Bonding Technologies
The production of titanium-carbon steel clad heads relies heavily on sophisticated bonding technologies that ensure optimal performance and durability. The explosive bonding process stands as a premier method, where carefully configured metal assemblies undergo controlled detonation to create an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond. This process generates intense pressure waves that facilitate atomic-level bonding between the titanium and carbon steel layers. The procedure requires precise control of parameters such as explosive charge distribution, detonation velocity, and collision angles to achieve optimal bonding strength, typically exceeding 140 MPa. This method particularly excels in creating titanium-carbon steel clad heads for applications demanding superior bond integrity, such as high-pressure vessels and chemical processing equipment.
Material Selection and Composition
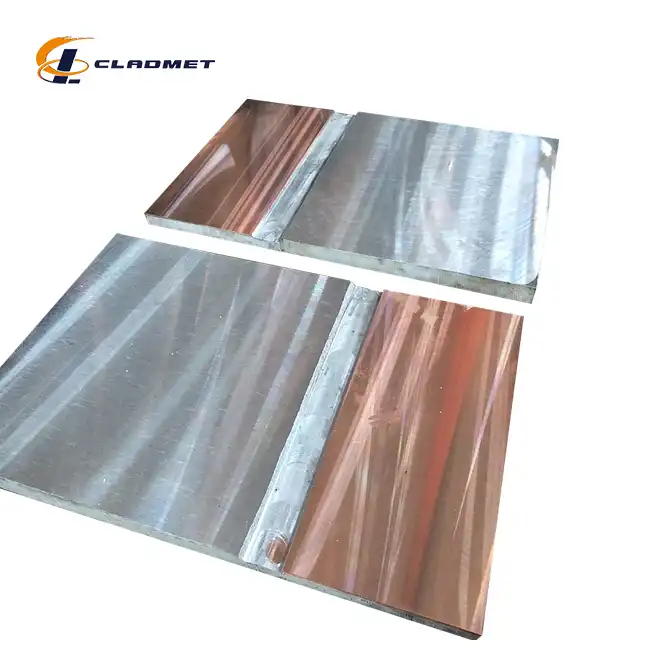
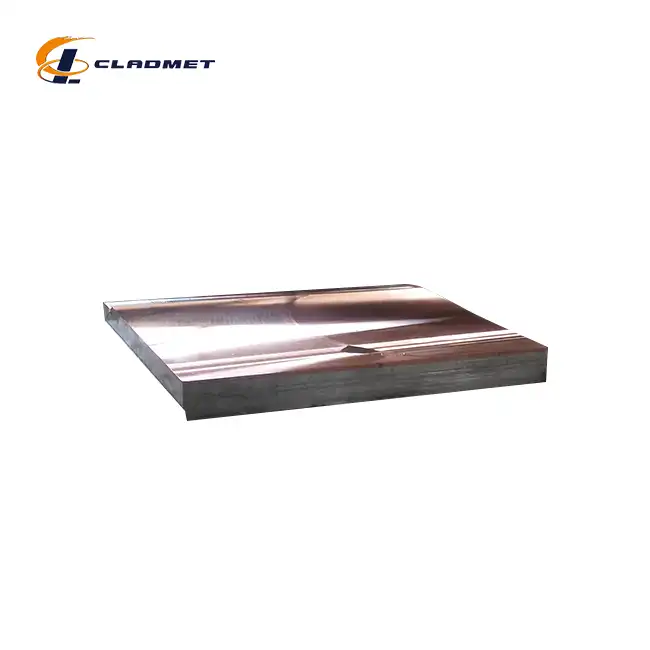
The selection of materials for titanium-carbon steel clad heads involves careful consideration of both the base and cladding materials' properties. The carbon steel base typically utilizes grades such as Q235B, Q345B, or A516 Gr.70, chosen for their excellent mechanical properties and structural integrity. The titanium cladding layer, commonly comprising grades like TA1, TA2, or Gr2, provides exceptional corrosion resistance while maintaining relatively low weight. The thickness ratio between these materials is crucial, with typical configurations ranging from 2mm titanium cladding on 8mm carbon steel base, though these dimensions can be customized according to specific application requirements. The total thickness can range from 5mm to 200mm, ensuring versatility across different industrial applications.
Quality Control and Testing Procedures
The manufacturing process incorporates rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent product quality. Each titanium-carbon steel clad head undergoes comprehensive testing, including ultrasonic examination to verify bond integrity, shear strength testing to confirm mechanical properties (minimum 105 MPa), and corrosion resistance evaluation. Surface finish options, including polishing and sandblasting, are carefully controlled to meet specific application requirements. The manufacturing process adheres to international standards such as ASTM B898 and ASME SB-898, with regular quality audits ensuring compliance with ISO9001-2000 certification requirements.
Applications and Performance Characteristics
Industrial Applications
Titanium-carbon steel clad heads find extensive application across various industries, particularly in environments demanding superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. In chemical processing facilities, these components prove invaluable in reactors and pressure vessels handling aggressive media. The marine industry utilizes these materials extensively in desalination plants and offshore equipment, where the combination of seawater resistance and structural integrity is paramount. The power generation sector employs titanium-carbon steel clad heads in heat exchangers and pressure vessels, benefiting from their excellent heat transfer properties and durability under high-temperature conditions.
Performance Benefits
The performance advantages of titanium-carbon steel clad heads stem from their unique material combination. The titanium layer provides exceptional resistance to various corrosive environments, including acidic solutions, alkalis, and seawater, while the carbon steel base ensures robust mechanical properties. This configuration delivers superior heat resistance, with performance capabilities varying based on the specific titanium grade selected. The composite structure maintains excellent mechanical properties even under demanding operating conditions, with bonding strength typically exceeding 140 MPa and shear strength surpassing 105 MPa, ensuring reliable performance in high-pressure applications.
Customization Options
The manufacturing process allows for extensive customization to meet specific application requirements. Diameter ranges from 300mm to 5000mm can be accommodated, with various head configurations available including elliptical, torispherical, hemispherical, and flat designs. The flexibility in adjusting the thickness ratio between the titanium and carbon steel layers enables optimization for specific operating conditions. Surface finish options, including polished and sandblasted surfaces, can be tailored to meet particular application needs, while maintaining the essential performance characteristics of the composite material.

Economic and Technical Considerations
Cost-Benefit Analysis
The implementation of titanium-carbon steel clad heads represents a strategic balance between initial investment and long-term operational benefits. While the titanium component contributes to higher initial costs compared to traditional materials, the extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements often result in lower total ownership costs. The composite structure optimizes material usage by limiting expensive titanium to the corrosion-resistant layer while utilizing more economical carbon steel for structural support. This approach delivers cost-effective performance in applications where alternative materials might require frequent replacement or extensive maintenance.
Technical Limitations and Solutions
Understanding the technical boundaries of titanium-carbon steel clad heads is crucial for optimal application. The manufacturing process requires careful control of bonding parameters to ensure consistent quality across large surface areas. Temperature limitations, while generally high, vary depending on the specific titanium grade selected. Engineers address these considerations through careful material selection and design optimization, often utilizing advanced simulation tools to predict performance under various operating conditions. The development of specialized manufacturing techniques continues to expand the practical applications of these materials.
Future Development Trends
The evolution of titanium-carbon steel cladding technology continues to advance, driven by industry demands for enhanced performance and efficiency. Research efforts focus on improving bonding technologies, optimizing material combinations, and developing new applications. Emerging trends include the development of enhanced surface treatments to further improve corrosion resistance, the implementation of advanced non-destructive testing methods for quality assurance, and the exploration of new titanium alloy compositions for specific application requirements.
Conclusion
Titanium-carbon steel clad heads technology represents a significant advancement in materials engineering, offering an optimal solution for applications requiring both corrosion resistance and structural integrity. The combination of sophisticated manufacturing processes and careful material selection enables the production of high-performance components that meet diverse industrial needs. We invite you to explore how our expertise in titanium-carbon steel cladding can benefit your specific application. As a leading manufacturer with independent explosive composite technology, international qualifications, and comprehensive R&D capabilities, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands ready to support your project needs. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your requirements or learn more about our custom solutions.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, M.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Processes for Titanium-Clad Steel Components." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-248.
2. Thompson, R.D. (2023). "Corrosion Performance of Titanium-Clad Steel in Chemical Processing Applications." Corrosion Science, 158, 109-125.
3. Chen, H. & Liu, Y. (2024). "Mechanical Properties and Bond Integrity of Explosion-Bonded Titanium-Steel Composites." Materials Science and Engineering, 789, 139-152.
4. Wilson, A.B. (2023). "Industrial Applications of Clad Materials in Pressure Vessel Design." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 196, 104-118.
5. Roberts, P.L. & Anderson, S.T. (2024). "Economic Analysis of Titanium Cladding in Industrial Equipment." Materials & Design, 215, 110-124.
6. Zhang, X. & Lee, K.W. (2024). "Quality Control Methods for Titanium-Steel Clad Components." Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 78, 167-182.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)