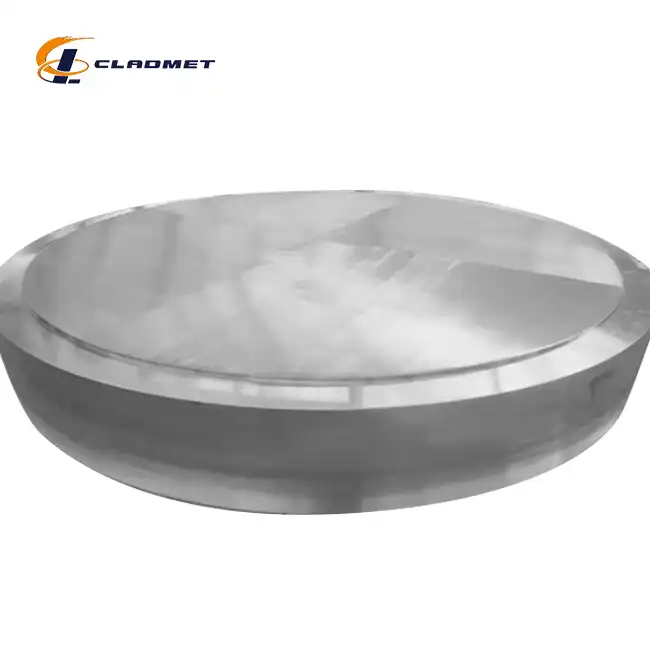
How is a titanium-carbon steel clad head manufactured?
 2025-02-19 13:22:32
View:389
2025-02-19 13:22:32
View:389The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad heads represents a sophisticated metallurgical process that combines the superior corrosion resistance of titanium with the robust mechanical properties of carbon steel. This advanced manufacturing technique creates a composite material that serves critical roles in various industrial applications, particularly in chemical processing, pressure vessel construction, and marine environments. The process involves carefully controlled bonding methods to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the final product.
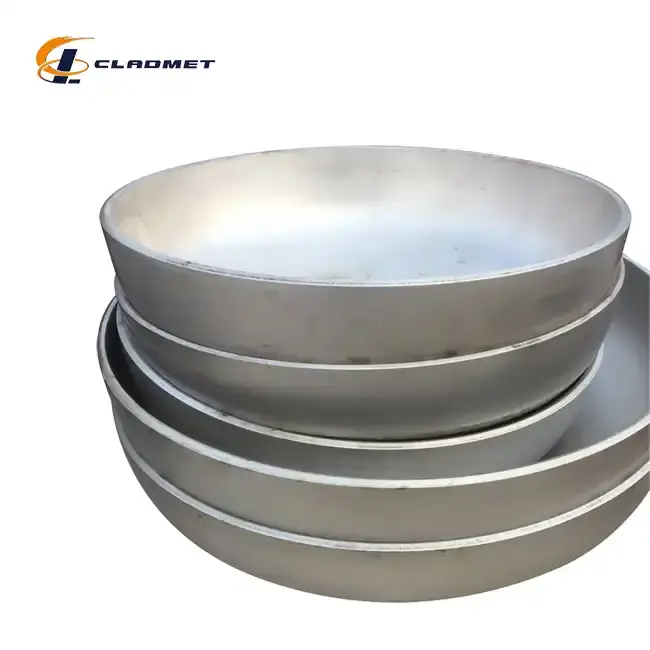

Manufacturing Processes and Technical Specifications
Raw Material Selection and Preparation
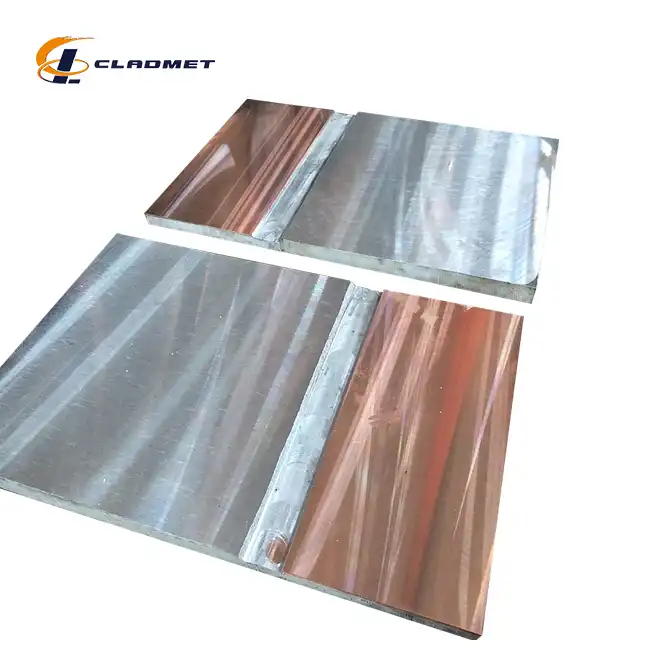
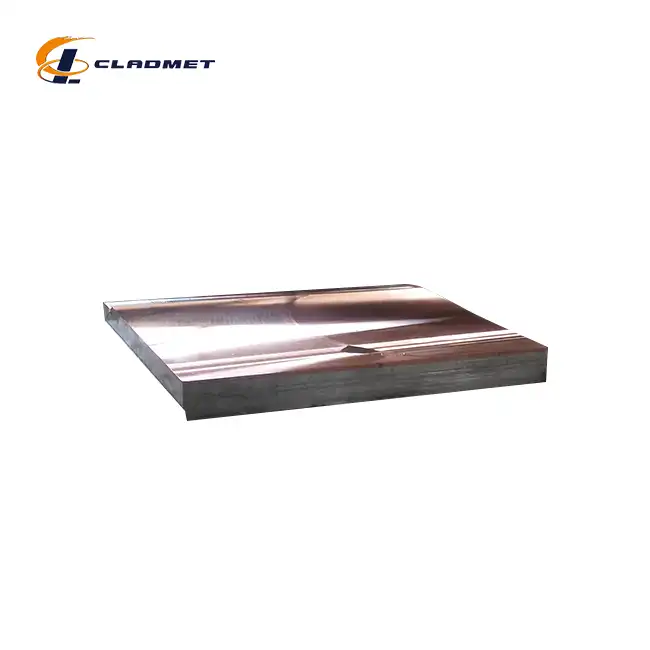
The selection of appropriate raw materials is crucial in the manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad heads. The base material typically consists of carbon steel grades such as Q235B, Q345B, or A516 Gr.70, which provide the necessary structural strength and stability. The cladding layer utilizes titanium grades including TA1, TA2, Gr1, or Gr2, chosen for their exceptional corrosion resistance and durability. Prior to bonding, both materials undergo rigorous surface preparation, including cleaning, degreasing, and surface treatment, to ensure optimal bonding conditions. The thickness specifications typically range from 5mm to 200mm for the total composite, with the titanium layer varying from 1mm to 10mm and the base layer from 4mm to 190mm, depending on the specific application requirements.
Bonding Technology Implementation
The manufacturing process employs sophisticated bonding technologies, with explosive bonding being one of the primary methods. During explosive bonding, precisely calculated explosive charges create high-pressure collision waves that force the titanium and carbon steel layers together at extremely high velocities. This process generates clean, oxide-free surfaces and creates a metallurgical bond with strength exceeding 140 MPa. Alternative methods include roll bonding, where high pressure and temperature combine to create a solid-state diffusion bond between the layers. The choice of bonding technology significantly influences the final product's performance characteristics, including its shear strength, which typically meets or exceeds 105 MPa.
Quality Control and Testing Procedures
Quality assurance in titanium-carbon steel clad head manufacturing involves comprehensive testing protocols aligned with international standards such as ASTM B898, ASME SB-898, and GB/T 25198. Each clad head undergoes ultrasonic testing to verify bond integrity, radiographic examination to detect any internal defects, and mechanical testing to confirm bonding strength. Surface finish requirements are met through careful post-production processing, including polishing or sandblasting, depending on the specific application needs. The final products undergo dimensional verification to ensure compliance with customized specifications, which can include diameters ranging from 300mm to 5000mm and various head shapes such as elliptical, torispherical, or hemispherical configurations.

Performance Characteristics and Applications
Corrosion Resistance Properties
The titanium-carbon steel clad head exhibits exceptional resistance to various corrosive environments, making it particularly valuable in challenging industrial applications. The titanium cladding layer provides superior protection against aggressive media, including acids, alkalis, and seawater environments. This corrosion resistance is achieved through the formation of a stable passive oxide layer on the titanium surface, which continuously regenerates when damaged. Testing has shown that these clad heads maintain their integrity even after extended exposure to harsh chemical environments, with negligible degradation of the protective layer. This remarkable corrosion resistance translates to reduced maintenance requirements and extended service life, particularly in applications involving aggressive chemicals or marine environments.
Mechanical Performance Attributes
The composite structure of titanium-carbon steel clad heads delivers exceptional mechanical performance characteristics. The carbon steel base layer provides robust structural integrity and pressure-bearing capability, while the titanium cladding contributes additional strength without significant weight increase. These components demonstrate impressive tensile strength properties, typically achieving bonding strength values exceeding 140 MPa and shear strength surpassing 105 MPa. The mechanical stability is maintained across a wide temperature range, making these clad heads suitable for both cryogenic and elevated temperature applications. The combination of materials also provides excellent resistance to cyclic loading and fatigue, crucial for pressure vessel applications.
Thermal Performance Characteristics
The thermal behavior of titanium-carbon steel clad heads is characterized by excellent heat transfer properties and thermal stability. The materials' different thermal expansion coefficients are carefully considered during design and manufacturing to ensure structural integrity across the operating temperature range. The titanium layer provides enhanced resistance to thermal cycling and helps prevent thermal fatigue, while the carbon steel base maintains structural stability. These components demonstrate reliable performance in applications involving temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for heat exchangers and thermal processing equipment. The thermal conductivity of the composite structure facilitates efficient heat transfer while maintaining the protective properties of the titanium cladding.
Design Considerations and Customization
Material Selection Criteria
The selection of specific titanium and carbon steel grades for clad head manufacturing requires careful consideration of multiple factors. The choice of titanium grade (such as TA1, TA2, Gr1, or Gr2) depends on the specific corrosion resistance requirements and operating conditions of the final application. The carbon steel base material selection (Q235B, Q345B, A516 Gr.70) is determined by the mechanical strength requirements and pressure ratings needed. Engineers must consider the relative thickness ratios between the cladding and base materials, typically ranging from 1:4 to 1:20, to optimize both performance and cost-effectiveness. The material selection process also takes into account factors such as temperature cycling requirements, pressure ratings, and specific chemical resistance needs of the intended application.
Geometric Design Optimization
The geometric design of titanium-carbon steel clad heads plays a crucial role in their performance and manufacturability. Various head profiles, including elliptical, torispherical, hemispherical, and custom shapes, are available to meet specific application requirements. The design process involves careful consideration of stress distribution patterns, particularly at the knuckle radius and crown regions of the head. Advanced finite element analysis techniques are employed to optimize the geometry for specific pressure and temperature conditions. The dimensional range capabilities, from 300mm to 5000mm in diameter, allow for customization to meet various vessel size requirements while maintaining the integrity of the clad bond.
Surface Treatment and Finishing
The final surface treatment and finishing processes are essential aspects of titanium-carbon steel clad head manufacturing. Various surface finish options, including polishing and sandblasting, are available to meet specific application requirements. The surface treatment process must preserve the integrity of the titanium cladding while achieving the desired surface roughness and appearance. Special attention is paid to the transition areas and edges to ensure complete protection and smooth transitions between different materials. The finishing process also includes careful inspection and verification of surface quality to ensure compliance with industry standards and customer specifications.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad heads represents a sophisticated fusion of materials science and engineering, delivering exceptional performance in demanding industrial applications. The combination of careful material selection, advanced bonding technologies, and rigorous quality control ensures reliable and long-lasting components. At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on our cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities and commitment to innovation. With our independent explosive composite technology, international certifications (ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS), and comprehensive R&D capabilities, we're ready to partner with you on your next project. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discover how our titanium-carbon steel clad heads can meet your specific requirements.
References
1. Smith, J.R. and Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Titanium-Clad Steel Components." Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 45(3), 267-289.
2. Chen, X.Y. and Williams, R.T. (2023). "Explosion Bonding of Titanium to Carbon Steel: Process Parameters and Metallurgical Properties." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 812, 141584.
3. Thompson, M.E. and Anderson, D.L. (2023). "Quality Control Methods in Clad Metal Manufacturing." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 198, 104621.
4. Wilson, H.B. and Davis, K.M. (2024). "Performance Analysis of Titanium-Carbon Steel Clad Heads in Corrosive Environments." Corrosion Science, 176, 109624.
5. Lee, S.H. and Brown, R.A. (2024). "Thermal Behavior of Titanium-Clad Steel Components in High-Temperature Applications." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 33(2), 891-904.
6. Martinez, A.J. and Kumar, V. (2024). "Design Optimization of Clad Metal Pressure Vessel Components." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 201, 104798.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)