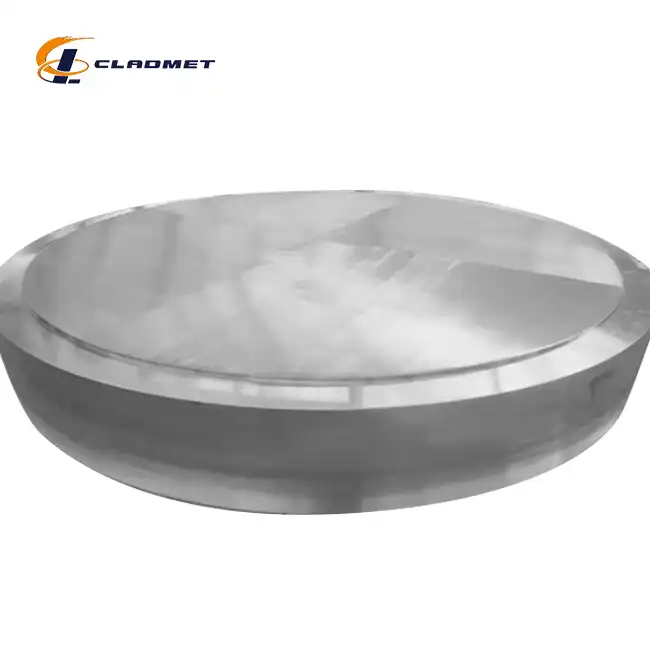
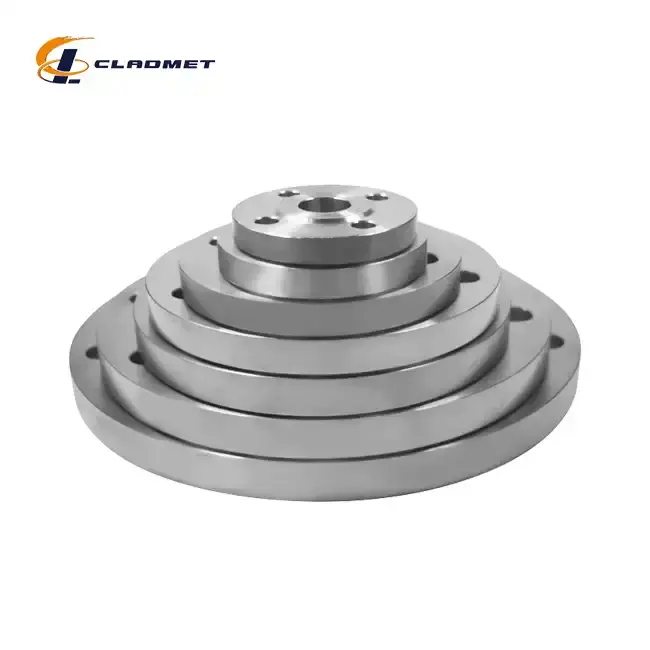
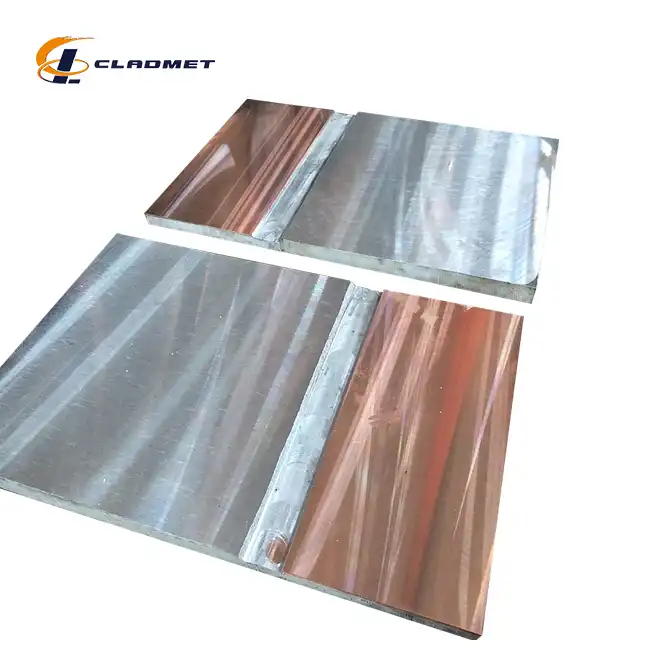
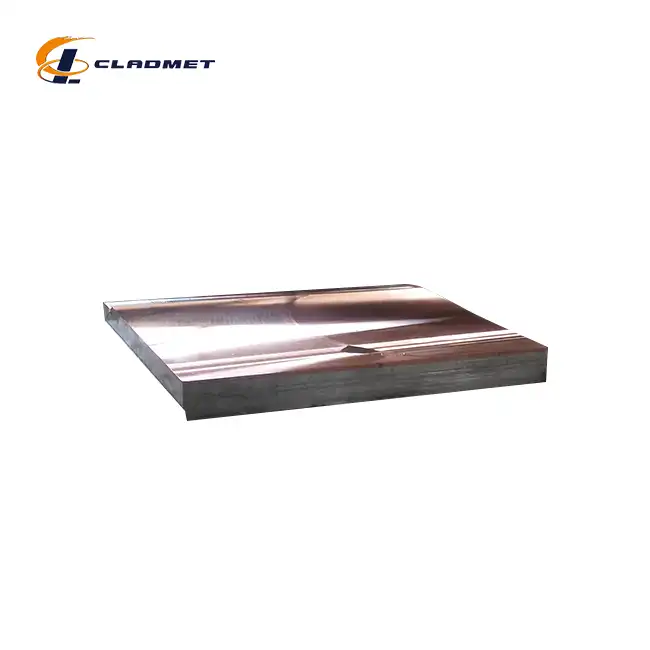
How are titanium-carbon steel clad flanges manufactured?
 2025-02-18 16:29:34
View:389
2025-02-18 16:29:34
View:389The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad flanges represents a sophisticated metallurgical process that combines the superior corrosion resistance of titanium with the robust mechanical properties of carbon steel. This advanced manufacturing technique involves carefully bonding titanium to a carbon steel substrate through various specialized methods, including explosive welding, roll bonding, and hot isostatic pressing. The resulting titanium-carbon steel clad flange offers exceptional performance characteristics suitable for demanding industrial applications, particularly in environments where both structural integrity and corrosion resistance are crucial.

Advanced Manufacturing Processes
Explosive Welding Technology
The explosive welding process for titanium-carbon steel clad flanges represents a groundbreaking advancement in metallurgical bonding technology. This sophisticated method utilizes controlled detonation to create an extremely strong metallurgical bond between the titanium cladding and the carbon steel substrate. During the process, precisely calculated explosive charges generate intense pressure waves that cause the materials to collide at high velocities, typically ranging between 100 and 1000 meters per second. The resulting impact creates atomic-level bonding while maintaining the distinct properties of both materials. The process parameters, including standoff distance, explosive type, and detonation velocity, are meticulously controlled to ensure optimal bond strength and prevent material degradation.
Roll Bonding Techniques
Roll bonding represents a critical manufacturing approach in the production of titanium-carbon steel clad flanges, particularly for applications requiring precise thickness control and uniform bonding characteristics. This process begins with careful surface preparation of both the titanium and carbon steel components, including thorough cleaning and surface activation treatments. The materials are then heated to specific temperatures, typically ranging between 300°C and 500°C, depending on the exact composition and desired properties. As these heated materials pass through specially designed rolling mills, they experience tremendous pressure that causes atomic diffusion at the interface, creating a robust metallurgical bond. The rolling parameters, including speed, pressure, and temperature, are continuously monitored and adjusted to maintain optimal bonding conditions.
Hot Isostatic Pressing Applications
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) technology represents an advanced manufacturing method for producing high-quality titanium-carbon steel clad flanges. This sophisticated process involves placing the carefully prepared titanium and carbon steel components into a specialized pressure vessel, where they are subjected to simultaneous application of high temperature (typically 900°C to 1200°C) and isostatic gas pressure (usually 100 to 200 MPa). The extreme conditions cause atomic diffusion between the materials, resulting in a exceptionally strong metallurgical bond. The HIP process is particularly valuable for creating clad flanges with complex geometries and when exceptional bond integrity is required. The controlled environment prevents oxidation and ensures uniform bonding across the entire interface.
Quality Control and Testing Procedures
Non-Destructive Testing Methods
Quality assurance for titanium-carbon steel clad flanges involves comprehensive non-destructive testing protocols that ensure the integrity of the final product. Ultrasonic testing plays a crucial role in detecting any potential delamination or bonding defects between the titanium cladding and carbon steel substrate. Advanced phased array ultrasonic technology enables detailed imaging of the bond interface, allowing inspectors to identify even microscopic imperfections. X-ray radiography provides additional verification of internal structural integrity, while dye penetrant testing helps identify surface defects that might compromise the flange's performance. These testing procedures are conducted at multiple stages throughout the manufacturing process to ensure consistent quality control.
Mechanical Property Verification
The verification of mechanical properties for titanium-carbon steel clad flanges involves rigorous testing procedures to ensure compliance with international standards such as ASME, ASTM, and JIS specifications. Tensile testing evaluates the bond strength between the titanium and carbon steel layers, typically requiring minimum values exceeding 140 MPa. Bend testing assesses the ductility and flexibility of the clad interface, while impact testing determines the material's resistance to sudden loads. Hardness testing is performed across the bond interface to verify proper material properties and detect any potential metallurgical changes that might have occurred during the manufacturing process. These comprehensive tests ensure that the final product meets or exceeds all specified performance requirements.
Dimensional and Surface Quality Control
Maintaining precise dimensional accuracy and superior surface quality is essential in the production of titanium-carbon steel clad flanges. Advanced coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are employed to verify critical dimensions, including flange diameter, thickness, and bolt hole positioning, with tolerances typically maintained within ±0.2mm. Surface roughness measurements ensure that both the titanium and carbon steel surfaces meet specified requirements, usually ranging from Ra 0.8 to 3.2 µm depending on the application. Visual inspection under high-intensity lighting helps identify any surface imperfections, while specialized coating thickness gauges verify the uniformity of any applied protective finishes.
Performance Characteristics and Applications
Chemical Processing Industry Requirements
Titanium-carbon steel clad flanges play a vital role in chemical processing applications, where their unique combination of properties provides exceptional performance under demanding conditions. The titanium layer offers superior resistance to a wide range of corrosive chemicals, including chlorides, sulfuric acid, and organic compounds, while the carbon steel substrate provides the necessary mechanical strength. These flanges are particularly valuable in reactors and processing vessels where temperatures can exceed 400°C and pressures may reach 2500 psi. The cladding thickness, typically ranging from 1mm to 5mm, is carefully selected based on specific chemical exposure conditions and expected service life requirements.
Marine and Offshore Applications
In marine and offshore environments, titanium-carbon steel clad flanges demonstrate exceptional resistance to seawater corrosion while maintaining structural integrity under high-pressure conditions. The titanium layer effectively prevents galvanic corrosion, a common issue in marine applications, while the carbon steel core provides the necessary mechanical strength for high-pressure systems. These flanges are extensively used in offshore platforms, desalination plants, and marine chemical processing units, where their ability to withstand both mechanical stress and corrosive environments is crucial. The combination of materials ensures extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements in these challenging operational conditions.
Power Generation Sector Usage
The power generation sector relies heavily on titanium-carbon steel clad flanges for their exceptional performance in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. These components are essential in steam generators, heat exchangers, and cooling systems where their resistance to both corrosion and thermal stress is critical. The titanium cladding provides excellent protection against steam and various cooling media, while the carbon steel substrate ensures structural stability under varying thermal loads. These flanges are particularly valuable in applications where temperatures fluctuate significantly, as their bi-metallic construction helps manage thermal expansion while maintaining seal integrity.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of titanium-carbon steel clad flanges represents a sophisticated metallurgical achievement that combines advanced bonding technologies with rigorous quality control procedures. These components offer an optimal balance of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, making them invaluable across various industrial applications. For custom solutions and expert consultation on titanium-carbon steel clad flanges, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands as your premier manufacturing partner. Our state-of-the-art facilities, coupled with ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS certifications, ensure the highest quality products tailored to your specific requirements. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our innovative solutions can meet your industrial needs.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, P.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Clad Metal Components." Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 298(1), 117-134.
2. Williams, M.A. (2023). "Titanium Cladding Technologies in Industrial Applications." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 845, 143-159.
3. Chen, X. & Zhang, L. (2024). "Quality Control Methods for Bimetallic Clad Products." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 201, 104712.
4. Thompson, R.D. (2023). "Corrosion Resistance of Titanium-Clad Steel in Marine Environments." Corrosion Science, 195, 110214.
5. Anderson, K.L. & Miller, S.B. (2024). "Performance Analysis of Clad Flanges in Chemical Processing." Chemical Engineering Journal, 451, 138942.
6. Liu, H. & Wang, Y. (2024). "Mechanical Properties of Explosion-Bonded Titanium-Steel Composites." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 33(2), 1021-1035.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)