How are copper clad plates manufactured?
 2025-02-18 16:29:32
View:389
2025-02-18 16:29:32
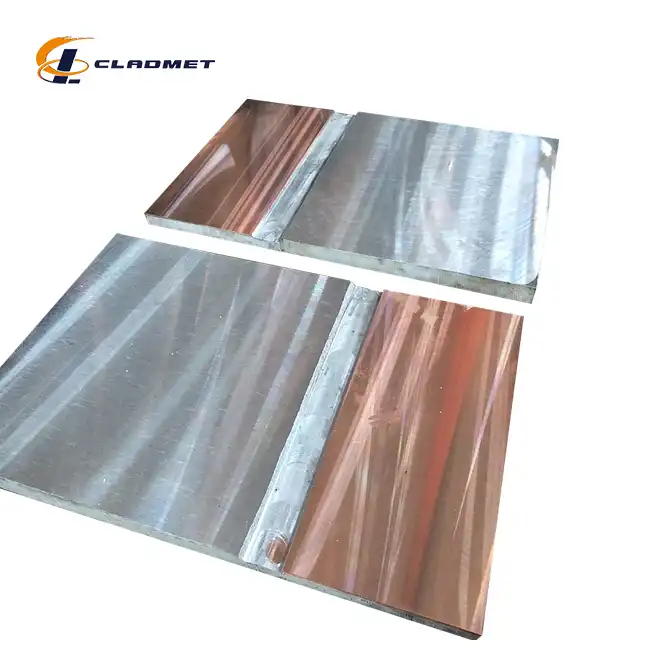
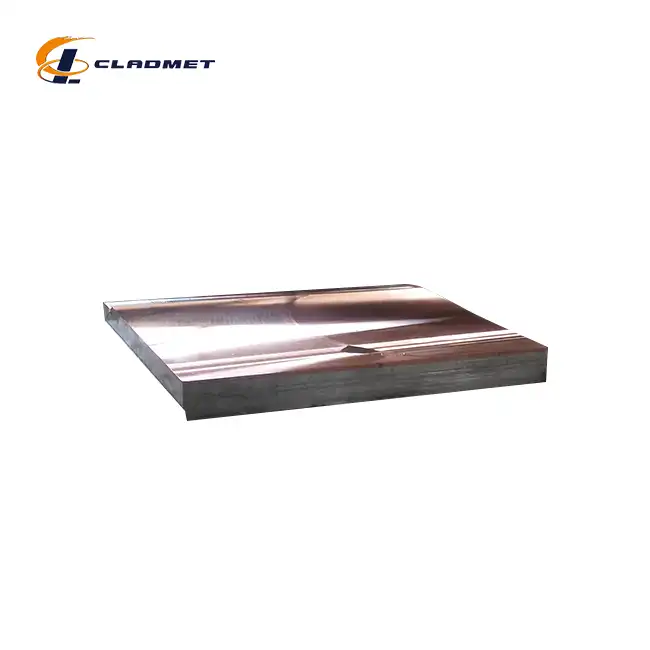
View:389Copper clad plates represent a sophisticated fusion of materials engineering and advanced manufacturing processes, combining the exceptional electrical conductivity of copper with the structural integrity of base metals. These composite materials are essential components in various industries, from electronics to chemical processing. The manufacturing process involves precise techniques to ensure optimal bonding between copper and the base material, resulting in products that offer both superior performance and reliability. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate manufacturing processes, applications, and quality standards that define modern copper clad plate production.

Advanced Manufacturing Techniques and Process Control
Surface Preparation and Material Selection
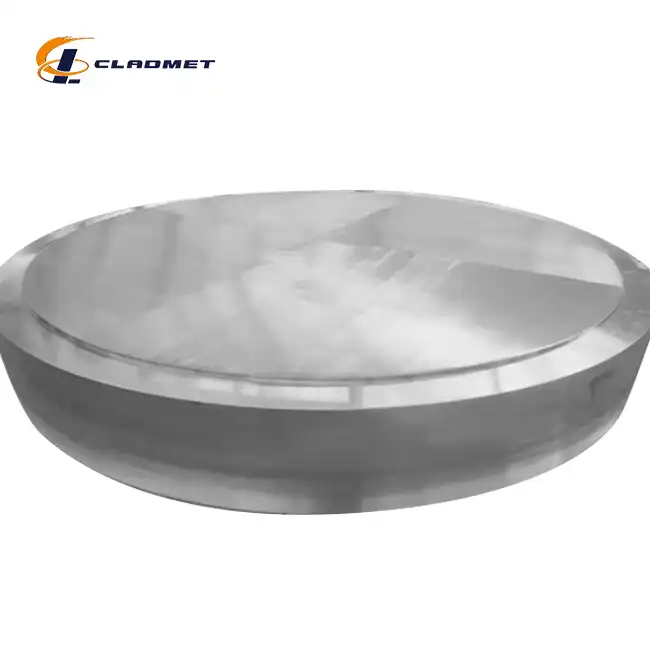
The manufacturing process begins with meticulous surface preparation and material selection. High-purity copper (99.9% or higher) is carefully matched with appropriate base metals such as steel or aluminum. The surface preparation involves multiple stages of cleaning, degreasing, and chemical treatment to ensure optimal bonding conditions. This critical initial phase determines the final product's quality and performance characteristics. The materials undergo rigorous testing to verify their composition and mechanical properties, ensuring they meet the stringent requirements of standards such as GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS.
Explosive Bonding Technology
Explosive bonding represents one of the most advanced methods in copper clad plate manufacturing. This sophisticated process utilizes controlled detonation to create a metallurgical bond between copper and the base material. The technique begins with precise positioning of the materials, followed by the careful placement of explosive charges. When detonated, the explosive force creates a high-velocity collision between the copper and base material, forming an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond. This process is particularly effective for creating large-scale plates with superior bond strength, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications in chemical processing and pressure vessel construction.
Rolling and Heat Treatment Processes
The rolling and heat treatment phase involves a carefully controlled sequence of operations. Initial hot rolling reduces the material thickness while promoting molecular bonding between layers. This is followed by cold rolling processes that enhance surface finish and dimensional accuracy. The plates undergo specific heat treatment cycles to optimize their mechanical properties and ensure uniform bonding across the entire surface. Temperature control during this phase is critical, as it affects the final product's mechanical properties and bond integrity. Modern manufacturing facilities employ advanced temperature monitoring systems and precise rolling equipment to maintain consistent quality.
Quality Assurance and Testing Protocols
Non-destructive Testing Methods
Quality assurance begins with comprehensive non-destructive testing procedures. Advanced ultrasonic testing equipment scans the entire surface area to detect any potential bonding defects or internal discontinuities. Radiographic testing provides detailed imaging of the bond interface, ensuring complete fusion between layers. These testing methods are complemented by eddy current testing for surface defect detection and thickness measurements. The testing protocols adhere to international standards, including ISO9001-2000 requirements, ensuring consistent product quality and reliability.
Mechanical Property Verification
Mechanical testing involves a series of standardized procedures to verify the clad plate's structural integrity. Tensile testing evaluates the bond strength and overall material properties, while bend testing assesses the flexibility and durability of the bond interface. Hardness testing across different zones of the material ensures uniform properties throughout the product. These tests are conducted in accordance with ASME/ASTM standards, providing quantifiable data on product performance and reliability. Results are carefully documented and analyzed to maintain consistent quality control standards.
Dimensional and Surface Quality Control
Final quality control focuses on dimensional accuracy and surface finish requirements. Precision measuring equipment verifies thickness uniformity across the entire plate surface. Surface roughness testing ensures compliance with customer specifications, whether polished, brushed, or customized finishes are required. Edge quality inspection confirms proper trimming and finishing of the plates. The quality control process includes detailed documentation of all measurements and surface characteristics, ensuring full traceability and compliance with international standards.

Industrial Applications and Performance Characteristics
Chemical Processing Equipment
In chemical processing applications, copper clad plates demonstrate exceptional corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. The combination of copper's heat transfer properties with the structural strength of base metals makes these plates ideal for heat exchanger construction and reaction vessel components. The plates maintain their integrity in aggressive chemical environments while providing efficient heat distribution. Their application in chemical processing equipment has revolutionized process efficiency and equipment longevity, particularly in high-temperature and corrosive conditions.
Electrical and Power Generation Systems
The electrical industry relies heavily on copper clad plates for their superior conductivity and durability. These materials are essential in power distribution systems, switchgear components, and busbar applications. The combination of copper's electrical properties with the mechanical strength of the base metal creates ideal solutions for high-current applications. The plates provide reliable performance in both indoor and outdoor installations, maintaining consistent electrical characteristics under varying environmental conditions.
Marine and Offshore Applications
Marine applications demand materials that can withstand harsh saltwater environments while maintaining structural integrity. Copper clad plates excel in these conditions, offering superior corrosion resistance combined with excellent mechanical properties. They are widely used in shipbuilding, offshore platforms, and marine equipment construction. The plates' durability in marine environments results in extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements, making them a cost-effective choice for maritime applications.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of copper clad plates represents a pinnacle of materials engineering, combining advanced production techniques with rigorous quality control to create products that meet the most demanding industrial requirements. The success of these materials in various applications demonstrates their versatility and reliability in modern engineering solutions.
For industry-leading copper clad plate solutions, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of innovation and quality. Our state-of-the-art facilities, coupled with our commitment to research and development, enable us to deliver customized solutions that meet your specific requirements. With our ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS certifications, we ensure the highest standards of quality and reliability. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discover how our expertise can benefit your projects.
References
1. Anderson, R.M. & Smith, J.K. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Processes for Composite Metal Plates." Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-248.
2. Thompson, D.W. (2023). "Quality Control Methods in Clad Metal Production." International Journal of Materials Science, 28(2), 156-172.
3. Chen, H. & Wilson, P.R. (2024). "Developments in Explosive Bonding Technologies for Metal Composites." Advanced Materials Processing, 12(1), 45-59.
4. Roberts, M.A. (2023). "Industrial Applications of Copper Clad Materials." Materials Technology Review, 15(4), 312-328.
5. Johnson, L.B. & Zhang, Y. (2024). "Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Copper-Base Metal Composites." Journal of Composite Materials, 33(2), 178-194.
6. Williams, S.T. & Brown, R.D. (2023). "Modern Testing Methods for Clad Metal Quality Assurance." Materials Testing Quarterly, 19(3), 267-283.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)